Re: Making
L4 Gallery, Southampton
13 February to 8 March, 2016
‘…what of the artists, the makers, how do they make decisions? …now an artist is as likely to atomise or extrude or draw, print, wear or perform with objects as part of an adaptable practice. And since art has been transformed into aesthetic communication it is no longer traditions but messages that count…’ – Ian Dawson, Making Contemporary Sculpture, 2012, p.9
‘I don’t think it makes sense to untangle the picture (as material) from the image (as immaterial). […] Somehow we get snagged by a desire, an objet petit ‘an’, to theorise the image as a singularity, rather than reimagining and enacting theory around its multiplicity.’ – Sunil Manghani, ‘Images: An Imaginary Problem’, 2011, p.228.
This exhibition documents three PhD seminars that each ran between 2-3 days at Winchester School of Art, University of Southampton. Underlying Re:Making is a consideration of what it means to make and re-make ideas, objects and processes. Each seminar centred around key prompts or challenges for collaborative engagement, but without necessarily stipulating required outcomes. Instead the sessions were intended as a open spaces to explore and experiment. Working together we can observe and draw upon the range of decisions we each seem to make intuitively as we approach the ‘research’ in hand. In part a response to Ian Dawson’s suggestion from a previous seminar, the aim was to work together, and intensively, to question what it is we do and think when making, writing and researching. Taken as a whole, Re: Making asserts we might need to make before we think as much as we think before we make.
Prompts were provided to explore different modalities of making as follows:
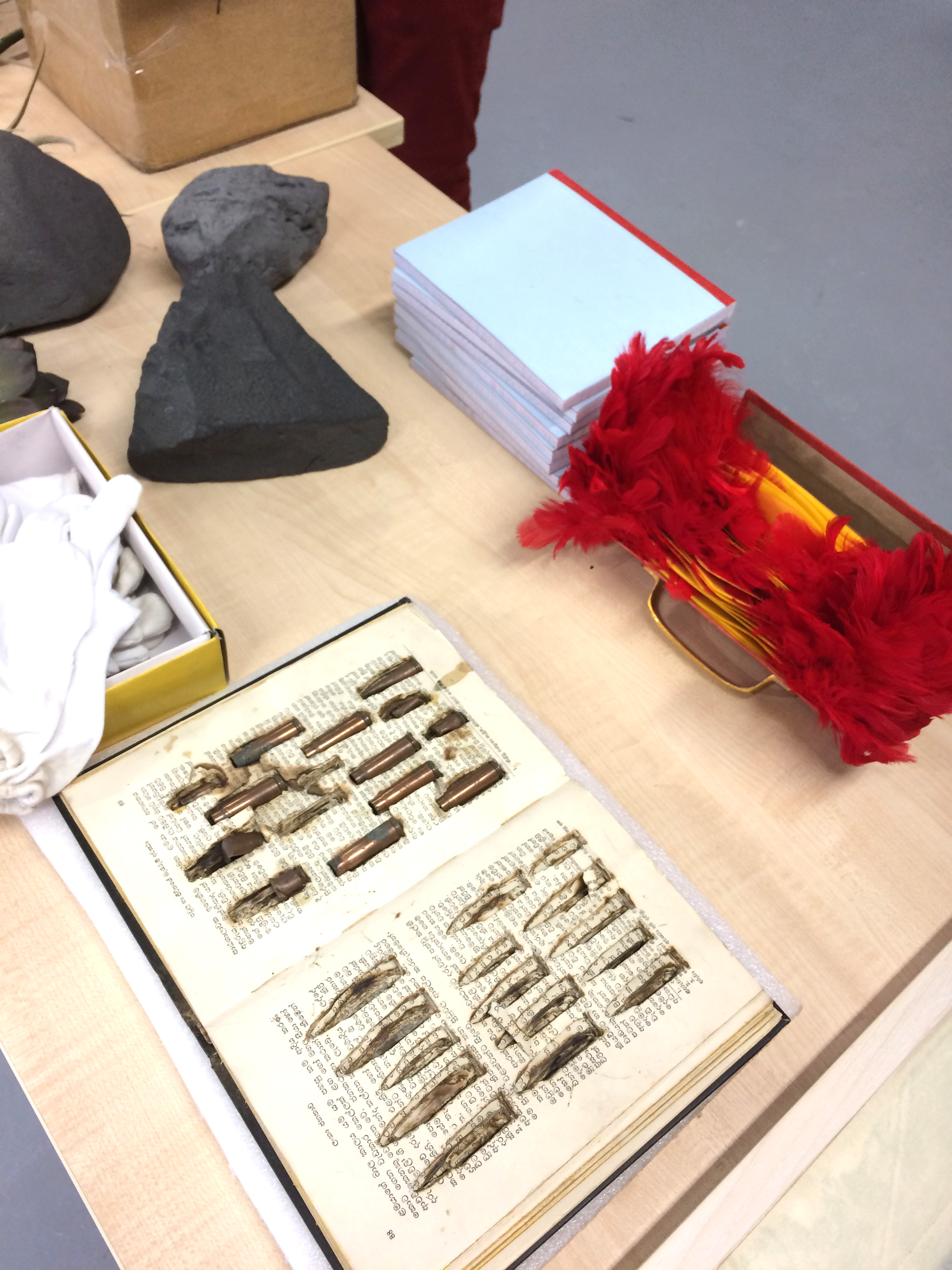
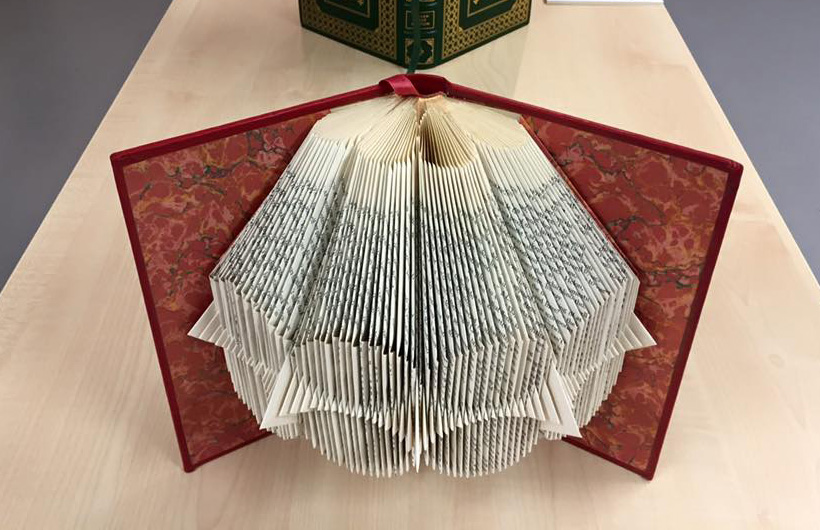
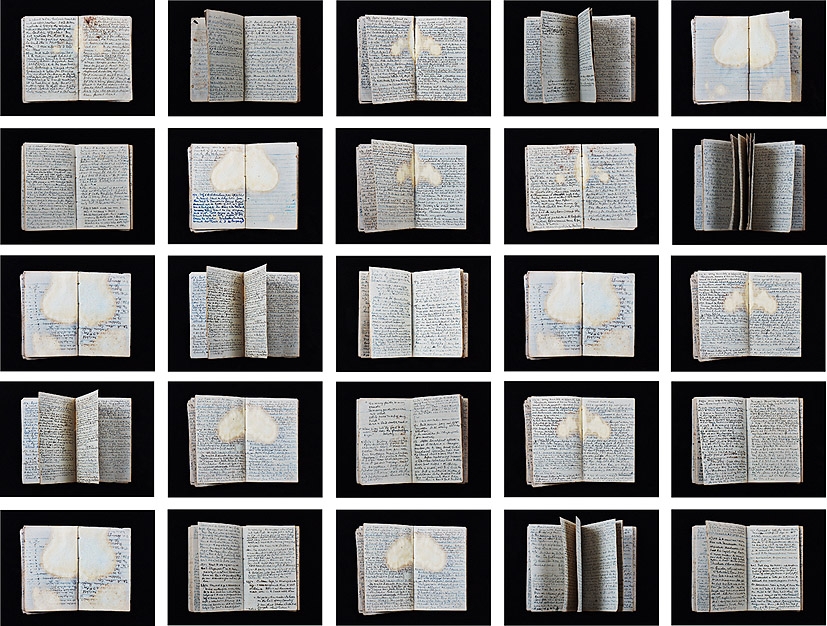
- Reading Room was the re-creation of an exhibition of artists’ books that had originally shown in India. The artworks were brought into dialogue with the School’s own collection so reframing and re-tracing thoughts, beliefs and emotions within the boundaries of a book and the cultures in which they circulate. In this case a 3-day seminar ran between Wednesday 28 and Friday 30 October 2015, with the Private View of the exhibition held in the evening of the final day. See more…
- Plastic Surgery (held on Tuesday 10 and Wednesday 11 November 2015) took two icons of ‘plastic pop’, Michael Jackson and Kylie Minogue, as ‘models’ to explore simultaneously both physical 3D rendering processes and conceptual understandings of plasticity as evoked by the fine arts and cultural critique. Taken together, Re: Making asserts we might need to make before we think as much as we think before we make. See more…
- Writing as Making was a study retreat for dedicated time to write, to share in the act of writing, and to reflect critically on various strategies. The seminar was held on Wednesday 9 and Thursday 10 December 2015. One outcome was a re-making of Walter Benajmin’s ‘The Writer’s Technique in Thirteen Theses’, which quickly reveals writing as practice, as a working and re-working of texts in pursuit of new thoughts, images and confluences. See more…
Of related interest, see also:
- Drawing Together – a participatory outdoor drawing event, co-orangised by Cheng-Chu Weng and Sunil Manghani. The event was held on Saturday 17 October 2015, 11am – 1pm at the Discovery Centre, in Winchester and was part of the wider programming for 10 Days, Winchester’s biennial, interdisciplinary, arts festival. Through the medium of chalk and shadows Drawing Together sought to bring people together in a shared act of drawing. Visitors to the Discovery Centre were invited to draw together as a means to draw each other together if only fleetingly, just as our shadows are mere fleeting images of ourselves. See More…
- Practices of Research – as a precursor to the Re: Making seminars, a collaborative exhibition, Image-Text-Object: Practices of Research, was held at the L4 Gallery in early 2014. The exhibition presented the work of 16 PhD students and two members of staff from Winchester School of Art (WSA). Taken together the works offered a series of images, texts and objects, helping to think about different ways of seeing, thinking, writing and making. See More…