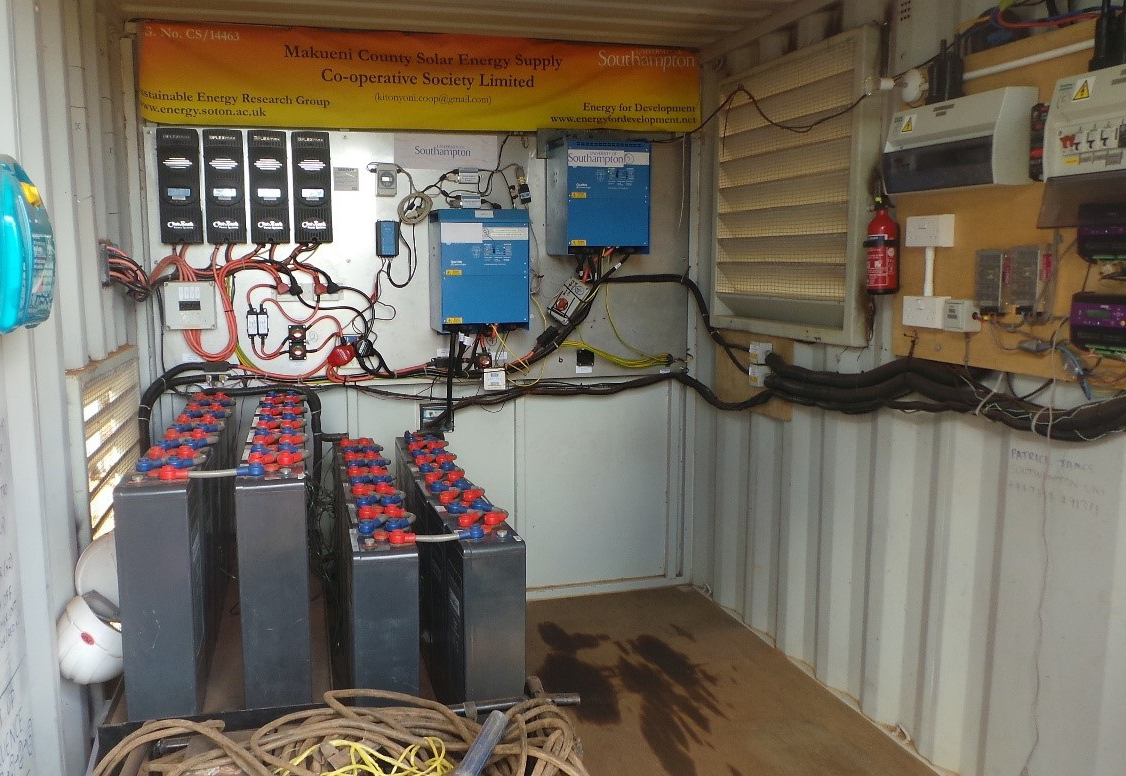
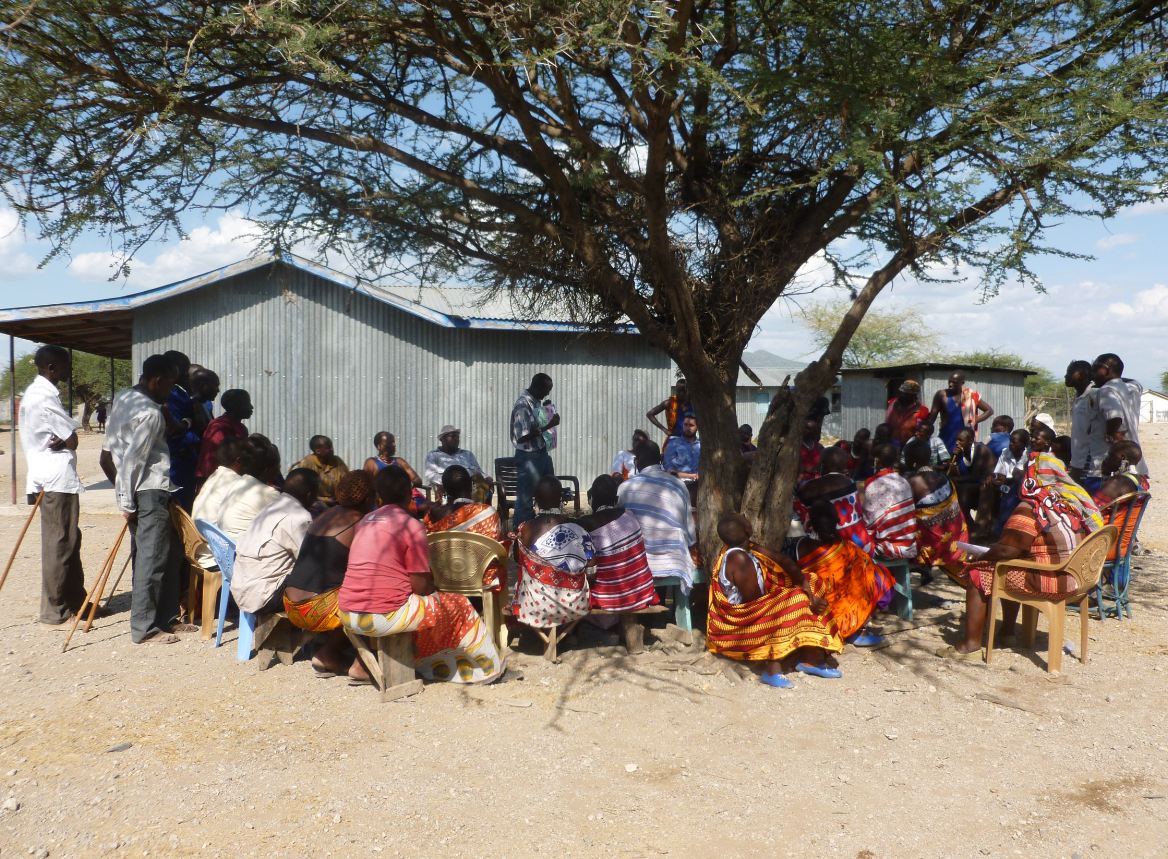
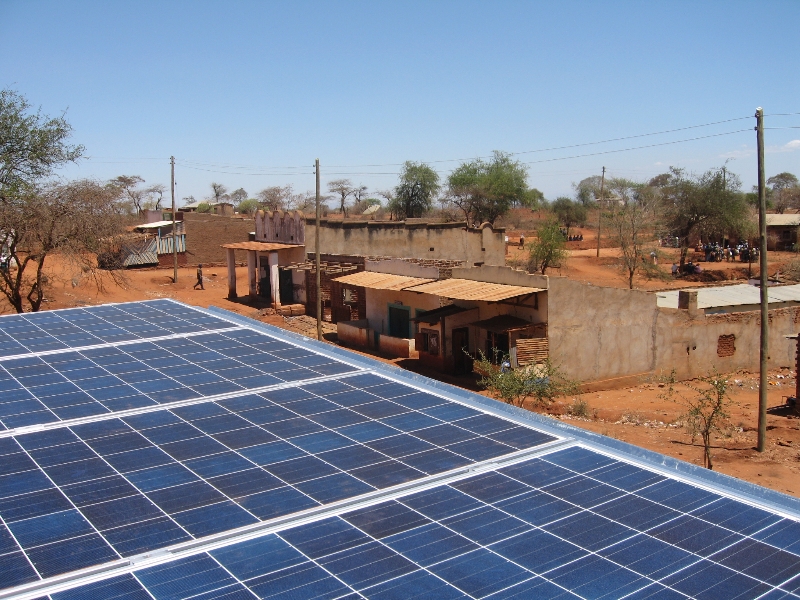
In Sub Saharan Africa around 600 million are without electricity. It is well recognised that mini grids are critical in addressing such electricity shortages providing access resulting in development and growth. Several countries such as Kenya and Uganda have large sections of their populations unconnected to the national grid. In order to provide needed access […]
Tag List: PV
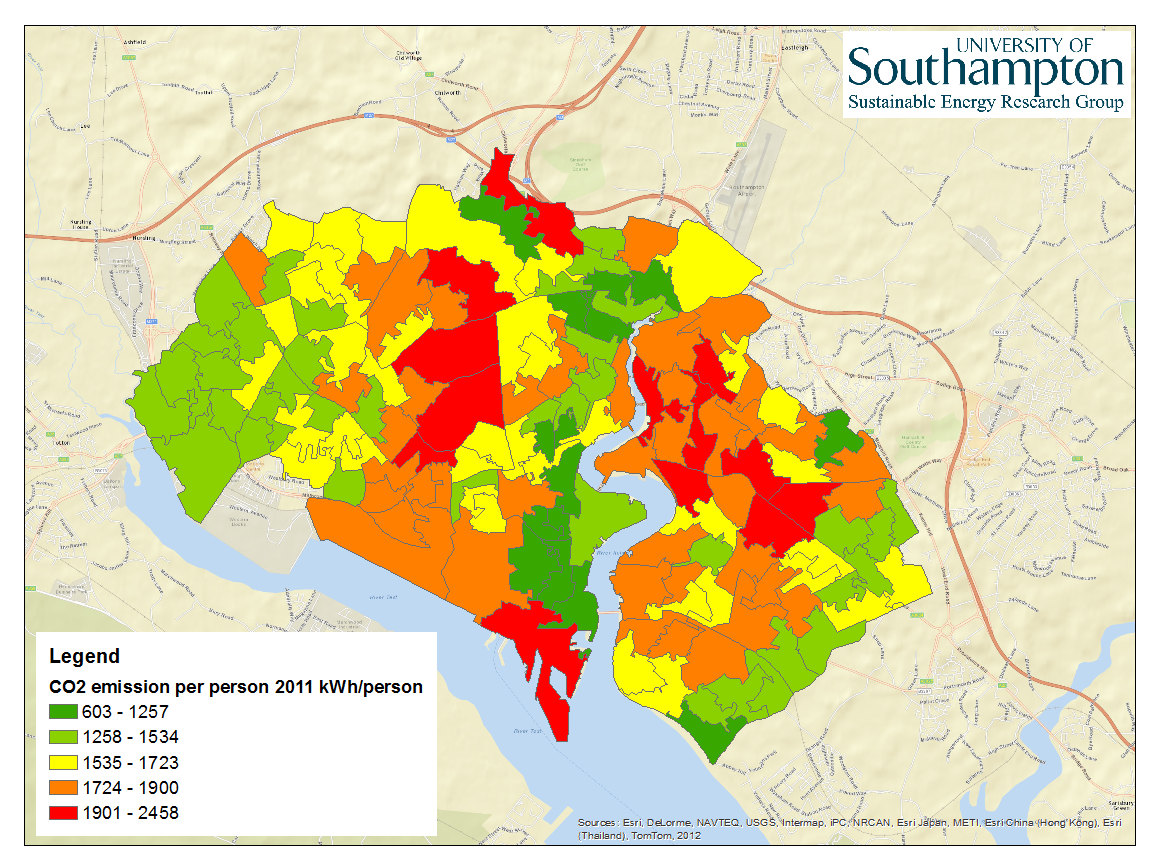
This app shows the results of modelling roof panel PV generation for non-domestic Southampton City Council properties in Southampton, UK. Click on the ‘Large Map’ button to see the full interaction version hosted by ESRI/ArcGIS. The three buttons on the top right corner of the map can be used to “Search”, “Filter”, and “Change basemap”. Results […]
The villages of Bambouti in Cameroon and Oloika in Kenya’s rift valley are set for electrification through PV array’s by the E4D team and partners. Baseline data has been collected and the villages will undergo installation in the coming months. Oloika, Kenya On a recent trip to Kenya, the E4D team, along with members of […]
Reliable and affordable sources of energy are fundamental not only for wellbeing, but also for economic growth and poverty reduction. Fulfilling the energy needs of developing countries without compromising the environment is a challenge, requiring imaginative policies and methods. Many rural communities do not have access to the national electricity network or the associated benefits […]
Residential grid connected PV systems are relatively simple to design with easy to predict annual yields. However, the headline economics of residential PV in the UK are at present unattractive. A typical small residential PV system (1 to 3 kWp) as shown in the top figure would cost in the year 2000 around £4,500 per […]
The University of Southampton has three permanently grid connected PV systems on its Highfield Campus designed and serviced by the Sustainable Energy Research Group. The installed capacity of these three facilities is about 20 kWp: (a) George Thomas Building – 12.2 kWp atrium (b) Building 2 – 7.2 kWp vertical façade (c) Eustice Building – […]
Silicon wafer solar cells have a low working voltage (~0.5 V) and so must be connected electrically in series to become useful. A ‘standard’ PV module consists of 36 cells in series, producing a maximum power point voltage of ~18 V suitable for charging a 12 V dc battery with a charge regulator. Grid connected […]
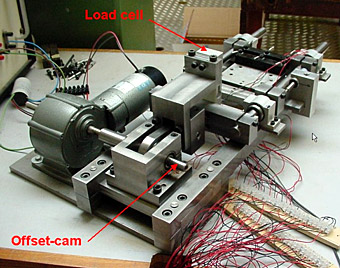
Background Photovoltaic modules have no moving parts and last upwards of 25 years with no maintenance aside from the occasional cleaning. Realising such a long lifetime for entire PV systems relies on the continued integrity of all system components. The installation of modules in building facades and other structures has necessitated the use of push […]
The Sustainable Energy Research Group has led a programme to develop what is believed to be the world’s first solar powered refrigeration unit installed on a working articulated vehicle for Sainsbury’s Supermarkets Ltd. Power for the refrigeration unit is generated by photovoltaic panels mounted on the trailer’s roof. An on-board battery stores the excess power for use by […]
Capital cost is the major issue and this impacts most directly on the size of a PV roof tile. For the ‘best integration’ a PV roof tile should be indentical in size and weight to a normal concrete tile. For example, a Marley Modern tile would provide an exposed area of 292 x 345 mm […]