Archive for the ‘web science’ tag
Introductions: Technoethics no comments
Moor on Ethics & Technology
Moor (2005) believed that with an increase in the social impact of technological advances, the number of ethical challenges also increase. He suggested that this is a result of the ever-increasing novel uses of technological advances and a lack of ethical inquiry into these activities. For example, the Web has fundamentally altered the social contexts within which we live, work and play. It has raised several questions including some about the legitimacy of human relationships maintained using its platform, its facilitation of illegal activity on a large scale and the privacy of its users.
However, though these are very present and pressing societal issues, they are also vast areas for investigation, and there is relatively sparse research coverage. Also, an added dimension to this challenge is that technological advances seem to continuously change the standard ethical questions. Thereby researchers are forced to simultaneously attempt to explore the ethical implications of these technologies as they were, are now and could be in the future.
Technoethics: Tackling New Types of Ethical Questions
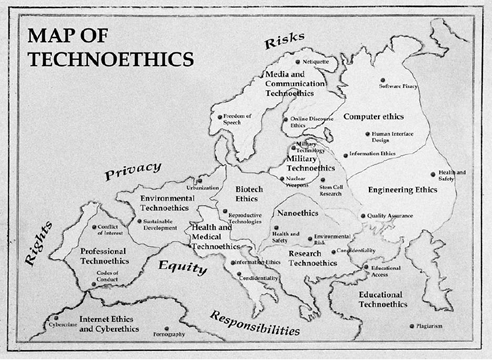
Unsurprisingly, many of the current debates surrounding technological advancement are addressed by technoethics (TE). They are some of the most challenging issues that scientists, innovators and technologists will face. These challenges usually characterise the roles these individuals play when plotting an ambitious route for the future. They inadvertently raise important questions about rights, privacy, responsibility and risk that must be adequately answered.
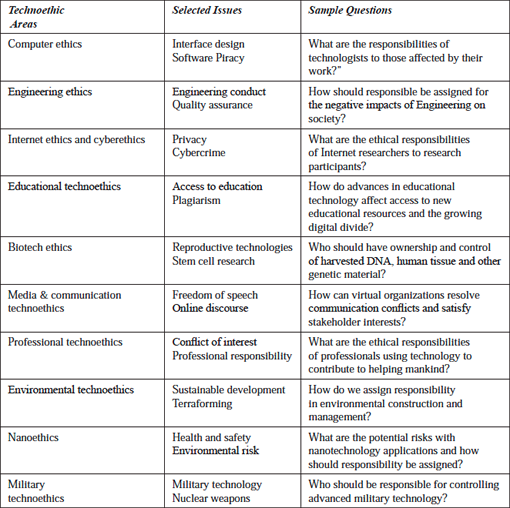
However, due to the variety of questions resulting in as much ethical inquiries that are based in different fields, there is a tendency for this knowledge to be somewhat disconnected. TE pulls this knowledge together around the central idea of technology. Moreover, unlike traditional applied ethics where focus is placed on an ethical concern for living things, TE is ‘biotechno-centric’. As the Web is to Web science, technology, as well as living things, are central in TE.
The Technoethics Way
Tracing its origins back to the late 1970s, TE emerged as an interdisciplinary field tasked with the job of answering the difficult questions posed earlier. Coined by Mario Bunge (1977), TE does not only assign technical responsibility to technologists but also gives them social and moral responsibility for their technological innovations and applications. It is believed that technologists are responsible for ensuring that their technologies are optimally efficient, not harmful and that its benefits are lasting.
This field distinguishes itself from other branches of applied ethics by elevating technology to the level of living things. However, it also builds on knowledge from wider ethical inquiry as well. TE has many sub-areas, for example, Internet, computer, biotech, cyber and nano ethics.
Calling All Web Scientists
Since the Web’s creation years ago, an understanding of this ever-changing phenomenon and its impact has been developing at a rapid pace in many disciplines. Yet there is a great deal more to learn, especially when the Web is positioned as the subject of focus. Considering Bunge’s views on technoethics, I believe that this obligation rests with Web scientists who are technically, morally and socially responsible for Web innovations and applications.

As a budding Web scientist, thinking about how technoethics applies to Web science, I am absolutely fascinated by all the very interesting questions that could be asked and that I could work towards answering. Ultimately, for us Web scientists, the aims of technoethics could be achieved by gaining insight into the relationship between people, the society and the Web, and how these entities impact each other.
Notes
This & Last Week’s Plan
Identifying the simplest books to read that will give an easy to understand introduction to the disciplines I picked.Making notes on books read.Prepare a blog post that gives an overview of what I want to work on.Publish a blog post that introduces technoethics.- Publish a blog post that introduces risk management.
Outline a reading plan for moving forward.
Introductory Readings
Ethics: A Very Short Introduction– Simon BlackburnHandbook fo Research on Technoethics– Rocci Luppicini & Rebecca AdellRisk: A Very Short Introduction– Baruch FischhoffFundamentals of Risk Management Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Risk Management– Paul Hopkin
Technoethics & Risk Management: Embracing The Web In The Workplace no comments

For some time I have been very interested in how people use the Web at work and the discussions surrounding this practice at different levels in the organisation. Over the years many have talked, written and passionately lobbied about the many issues that have emerged. I also joined this discussion and tried to present a balanced argument for the Web in the workplace, even if only for personal use. Yet, there still seems to be some confusion about how to best manage Web usage in organisations.
Taming the Web in the Caribbean Workplace
In the Caribbean, there is a predominantly negative perception of Web usage at work, especially among the management of large established organisations. There is a very real fear that Web usage in the workplace makes the organisation vulnerable to taking legal liability for related unlawful activities, security breaches, bandwidth drain and productivity losses. As a result, many organisations in the region have adopted an approach where they rather be safe than sorry. Unfortunately, based on my experience, measures used to manage risk are then usually excessive and outweigh the amount of risk posed.
Organisations have attempted to manage employee Web usage utilising several methods. Sometimes blocking and or requiring written permission to access certain sites and services, using monitoring software to enforce strict policies and providing training to employees on ‘proper’ Web usage in the workplace. However, barriers to unrestricted access are quickly being removed with the introduction of affordable 4G mobile Internet access and very strong adoption of smart phones (e.g., iPhone and Blackberry) by employees in the region. Unsurprisingly, this has prompted some organisations to respond by taking an even tougher approach to managing Web usage in the workplace on any device.
My Lens: Finding Responsible Ways to Embrace the Web in the Workplace
The above scenario, though somewhat extreme, does not only exist in the Caribbean region but is also likely to be present in organisations all over the world in varying forms. Given this, I have chosen to explore the disciplines of technoethics and risk management and their inherent approaches to the current issue. There is also hope to discover new ways organisations can go about creating effective strategies to encourage employees to use the Web at work in more responsible ways that does not put the organisation, themselves and the Web at risk.
Notes
This & Last Week’s Plan
Identify the simplest books to read that will give an easy to understand introduction to the disciplines you picked.- Make notes on books read.
Even if it is the last thing you do, prepare a blog post that gives an overview of what you want to work on by Monday.- Publish a blog post that introduces technoethics.
- Publish a blog post that introduces risk management.
- Outline a reading plan for moving forward.
Current Readings
- Ethics: A Very Short Introduction – Simon Blackburn
- Handbook of Research on Technoethics – Rocci Luppicini & Rebecca Adell
- Risk: A Very Short Introduction – Baruch Fischhoff
- Fundamentals of Risk Management Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Risk Management – Paul Hopkin
06 – Museology no comments
Museum Studies
The museums by themselves have different processes and meanings for the population and institutions. Through these classifications of museums, we can provide a more accurate linkage in between the object of study (or exhibited) and the audience.
Cultural Theory
Through contemporary cultural theory we can incorporate all sort of art practices into the everyday life. This will create our culture. So culture is becoming something less separatist in which art or culture itself no longer belongs to the educated or rich classes. The cultural theory is now being implemented more and more within museums, specially in social history and contemporary collections (Macdondald, 2011). Contemporary cultural theory seeks to utilize culture from a pluralistic perspective.
We inhabit a culture in the sense that we share a certain amount of knowledge and understanding about our environment with others.
We have evolved into a society that shares what Stuart Hall (1997: 18) in Macdonald (2011:18) defines “cultural maps” which makes us question or make judgements the value, status and legitimacy of products or cultural practices.
Within museums we are trying to materialize values and trying to give meaning to objects. For this reason museums within cultural theory are public spaces in which their values and the culture creation is always under debate.
Main theoretical apporach
In order to give meaning to something, we depend on a social construction of a signifying system that creates a shared understanding. The semiotic research of Ferdinand de Saussure, indicates that signifiers and signifieds relate arbitrarily. This means that perhaps the meaning or classification (curation) system to an object could be completely different from the perspective of a different culture.
When an artifact is being curated, this is attached or linked to an interpretation system that could be attached to a single cultural ‘string’. Taking the post-structuralist approach, we can provide a structure of interpretation that adapts to the cultural needs of the artifact or the audience. The attempt to materialize culture and present how an object can change through time, tends to fit to the vision of the post-structuralist thinking.
For this project this could be the way in which post-structuralism becomes the main way of presenting an object of study. A multi curated object presented from different cultural backgrounds and within different cultural audiences. Although the object can be presented with several meanings, “poststructuralist theory does not automatically imply that the material world ceases to exist” (Macdonald, 2011:21), but it will be understood from different perspectives or meanings.

V&A Mark Lane Archway (Gallery 49)
The Object
Before photography, multimedia and all the new technologies, the object by itself was the way to present the culture or places which it came from. For this reason I think that the object presented should contain enough information to communicate or represent the specific qualities of a culture. When the object is unique it will be a challenge to transmit the embedded information to a replica that could be presented somewhere else. The use of modern manufacture technology and prototype making can assist with this process. But it will be the correct adaptation of the object and its environment what will be able to make the correct communication to the audience possible.
Bibliography
MACDONALD, S. 2011. A companion to museum studies, Malden, MA ; Oxford, Wiley-Blackwell.
PEARCE, S. 2001. Interpreting Objects and Collections, Andover, Routledge, 2001.
05 – Information Systems no comments
Information Systems
O’brien (2007) defines an Information system (IS) as any kind of organized combination of people, hardware, software, communications network, data resources, and policies and procedures that stores, retrieves, transforms, and disseminates information in an organization.
The Framework.
There are 5 main areas that build the framework for the information systems. All these elements play an important role in the process of building the research project.

Foundation Concepts
To develop an information system, it is important to understand the behavioral, technical, business and managerial elements in order to develop the components for the Information System.
Information Technologies
In this area we will focus on the hardware, software, networks and data management that will affect the project in regard of its development, concept development and management.
Business Applications
Concepts like e-commerce can influence or provide ways of how the management can be implemented in an Information System like the one required for the Museum application.
Developments Processes
This will be focusing on the planning, development and implementation of the system(s) to meet the requirements of the problem or situation.
Management Challenges
Through this process, we will focus on delivering and managing effectively the information technologies at the end-user, business or int this case a multiuser/global institution.
Inside Management Systems
There are several types of Information Systems. They are usually classified into two different groups: Operations Support Systems and Management Support Systems.
Operation Support Systems:
- Specialized Processing Systems
- Transaction Processing Systems
- Process Control Systems
- Enterprise Collaboration Systems
Management Support Systems:
- Management Information Systems
- Decision Support Systems
- Executive Information Systems
- Specialized Processing Systems
There are five major resources focusing on the relationship with the IS and the products (O’brien, 2007)
- People Resources
- Specialists – software developers or system operators
- End Users – the person who uses the IS
- Hardware Resources
- Machines – computers, monitors, drives, printers or scanners
- Media – Storage, disks or paper forms
- Software Resources
- Programs – operating systems, editors or payroll applications
- Procedures – data entry procedures, error correction, paycheck distribution procedures
- Data Resources
- Communication media, communication processors, network access, control software
- Information Products
- Management reports, business visual display and paper forms
All these elements and areas can help us to visualize the complexity of the development of an Information System. We need to know what do we want from the organisation (system) to do? An organisation that includes people is more complex to manage than one that doesn’t (Wilson, 2001). For this, it is important to analyse the system implemented. Users or a human response will vary which will vary the judgement of the system.
To avoid judging problems we have to follow a specific methodology. We have to define a problem first of all. From here we can start gathering the appropriate techniques to solve this problem. The implementation or application of these techniques will allow us to go to the next step if effective or back to the previous one if unsuccessful. We also have to analyse the cost/effective solution. After these steps we can finally implement the solution.
So we have to solve a problem. But, who is defining the problem. What seems to be problematic for one person can not appar to be so for another one. Wilson (2001) explains that instead of focusing on a person’s problem or a problem, we have to focus on defining a situation that is problematic. I believe this will help the project not to isolate on a single person’s perspective.
Bibliography
O’BRIEN, J. A. & MARAKAS, G. M. 2007. Introduction to information systems, Boston, Mass., McGraw-Hill.
WILSON, B. B. 2001. Soft systems methodology conceptual model building and its contribution, Chichester ;, Wiley,.
04 – IT Modelling / Reporting Experiments (Statistics) no comments
Hypothesis and Experimentation
The scientific method
The hypothetico-deductive aspect of the scientific method focuses on the observation. This observation leads to a guess or logical guess called the hypothesis that tries to explain how a system works. From there, some predictions are made from this hypothesis and the experimentation or tests begin to try to prove it.
After the experimentation, the results can only be either consistent or inconsistent with the hypothesis.
These sets of experimentation will allow the hypothesis to be more consistent with the implementation of the project. But it is important to link the results properly with the hypothesis. This is where the statistics come in.
Statistics
Statistics are use in many different industries. Statistics will allow us to make decisions about large numbers of subjects which we can be able to group into some sort of systems. This way we can see patterns or data that is not visible through ‘static’ numbers.
It is extremely important to understand how statistics work. This is due to the necessity to analyse the information inside them. If we can not produce a proper statistical model, perhaps we won’t be able to make a good decision about our project. Also, if we can not understand statistics, there is no way we can see errors or disprove a theory or result.
Graphs
Once we have developed the statistical models we also have the option of visualizing this data. Or perhaps analyzing more in depth the information provided.
Mean, Error, Percent Error, and Percent Deviation
All these arithmetical/statistical tools can help us to understand our data. For example the Percent Deviation will allow us to understand or to see the whole extent of the data, not only the mean number.
| σ = |
|
Percent Deviation |
All statistical models are methods of obtaining the probability of success of our experiments which will help making a decision about our hypothesis or group analysis
Reporting Experiments
Through the report is where the explanation about the study. Peter Harris (2008) points 5 elemental items for the report.
- What you did
- Why you did it
- How you did it
- What were your findings
- What do you think it shows
This can then be translated to a formal document presentation like this:
- Title
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Method
- Results
- Discussion
- References
- Appendices
So, through this report we are intended to provide the information and the appropriate material. For this we also have to consider our reader. Who is intended to see our information. This is important because perhaps we will have to give an introduction to our area of study. If we are presenting the document to Computer Scientists, perhaps we need to give and induction to Heritage or Visual Communication.
Within museums
The statistics and the report provided is also an intrinsic part of the analysis. Before even starting to provide model experimentation, it is important to provide a hypothesis. Something like:
- What are the main reasons why small museums don’t have access to big collections?
- How many visitors does each museum have per year/per day/per month?
- How many times does an expensive collection travel through different museums?
It is important to start analyzing this type of information in order to visualize the real requirements not only of the project but also of the museum. problem or situation.
Bibliography
Brookshear, J. G. (2010). Computer science an overview. (11th ed.). Addison-Wesley,.
Harris, P. (Peter R. ). (2008). Designing and reporting experiments in psychology (3rd ed., p. 284). Maidenhead :: Open University Press,
McKillup, S. (2006). Statistics explained an introductory guide for life sciences (p. 267). Cambridge :: Cambridge University Press
03 – Museum collaboration // Collaborative Projects no comments
Collaborating with other disciplines
Starting from the essential bibliography for this research, there are some elemental concepts that the readings from Frederick Brooks (1995), Peter Harris (2008) and Brian Wilson (2001). The methodological process to undertake this project will be very important. The interdisciplinary quality will bring big challenges in the managerial aspect of the project. At this early stage, I believe the project being an intrinsic part of Web Science will invite collaborative work from Computer Science, Museology, Business Management and Visual Communication among others.
Developing Software?
I will argue that the project will contain a product similar to a computer software product. This product I believe will be develop similar to software, by this I mean a “collection of programs and the algorithms they represent” (Brookshear, 2010).
The complexity within the development of any kind of software of application requires an understanding of the methodology and the environment in which these products are created. It is also important to learn how to communicate with the team and how to make the team communicate with each other as a managerial task (Brooks, 1995). In the development of software, Brooks (1995) defines some essential tasks:
- Planning
- Coding
- Component test and early system test
- System test, all components in hand
Its about time!
It is important to know how to calculate the time needed for the development of the project and the time needed for each one of the tasks, not only for the implementation of these digital tools, but also for all the research tasks of the project. If there are some ‘hold backs’ within the project, Brooks (1995) explains that bringing more man work will not only be the solutions due to the tasks required for the development of software. Therefore it is important to analyse and understand all the different solutions applied within the Computer Science discipline and all the other disciplines involved.
It is recommended to use as little people as possible for the construction of a ‘soft system’. This is due to the managerial problems that big teams create. But sometimes small teams won’t be able to cope with the workload. Based on this, I will argue that it is also important to plan correctly the size of the teams in order for the research project to flow smoothly and with minimum communicative problems.
Assembling the team
It is my perception that is important to understand how a big system team is built in order to continue or to blend the methodological process into that work structure.
Although there are other organizational proposals, the one that seems more traditional is where we find a chief programmer defining the original program and codes and even testing the software. Followed by a co-pilot working as a second hand. There are other team members like the administrator, the editor, secretaries, program clerk, toolsmith, language lawyer and the tester (Brooks, 1995).
Problem solving
The main objective of a program or software is to solve a problem (Brooks, 1995; Wilson, 2001; Harris, 2008). For this it is essential to define the problem. What is this set of tools or applications going to solve. Wilson (2001), defines two types of problems: hard problems and soft problems. “The design of a piece of software to meet a given specification is a hard problem (as long as the specification is ‘a given’) whereas the specification of information requirements to meet business needs is a soft problem…”. The perception of what is a problems is also important. Being a multidisciplinary project means that what seems to be a problem, it could not mean anything to the person working in the museum or the audience or even the cultural heritage manager. To solve this, Wilson (2001) suggest that instead of trying to solve a problem, it would be more helpful to try to solve the situation that is creating the problem. For this he proposes the next methodology.
- Define the situation that is problematic
- Express the situation (top mapping, rich picture, etc.)
- Select concepts that may be relevant
- Assemble concepts into an intellectual structure
- Use this structure to explore the situation
- Define changes to the situation (i.e problems to be tackled)
- Implement change processes
Its all about the good manners.

Both Wilson (2001) and Brooks (1995) express the importance of the way to communicate with other team members. The ‘hierarchical’ level of communication. During the production of this research project (and any other), which I completely agree is to break the ‘tree’ system in which one person is the boss and the people below are reporting or working for this person. The responsibilities have been already defined and in the communicative structure, everybody is allowed to participate and to provide solutions to the situation problem solving.
Read the rest of this entry »
02 – Museum collaboration (bibliography) no comments
Museum collaboration // Essential bibliography
In this post I will start to list some of the bibliography to be used to get familiarized with essential concepts and ideas that will allow the project to be carried in the most optimal manner. The bibliography was chosen from the BSc Information Technology in Organizations fron University of Southampton and readings from Museum Studies and Museology.
Due to my visual communication background the Museum Studies readings I will be focusing on the more challenging theories instead on the basic methodology. On the other hand, IT in Organizations I will be focusing on basic readings to be able to get familiarized with basic concepts.
Information Technologies in Organizations
Tools and Techniques for IT Modeling
- Peter Harris. Designing and Reporting Experiments in Psychology (2nd ed). OU Press
- Steve McKillup. Statics Explained. Cambridge
Collaborative Projects
- Brooks, FP, The Mythical Man-Month, Addison-Wesley, 1982.
- Checkland, P, and Scholes, J, Soft Systems Methodology, Wiley
Human Computer Interaction
- Dix A, Finlay J, Abowd G and Beale R, Human-Computer Interaction, 3rd Edition. Prentice Hall, 2003
- Norman DA, The Design of Everyday Things, Basic Books, 2002 new edition
Information Systems Strategy
- Bocij, P. et al. (2005) Business Information Systems Technology, Development and Management in E-business. Pearson Higher Education FT Prentice Hall.
- Turban, E., Rainer, R.K. and Potter, R.E. 3rd editon (2004) Introduction to Information Technology: John Wiley and Sons
- Brown, J.S. and Duguid, P. (2002) The Social Life of Information. Harvard Business School
- Simon, J.C. (2000) Introduction to Information Systems. New York: Wiley
Museology and Museum Studies
- Sharon Macdonald. A Companion to Museum Studies, Malden, MA ; Oxford : Blackwell Pub., 2006
- Pearce, Susan. Interpreting Objects and Collections. Andover:Routledge, 2001
- Hein, George E. Learning in the Museum (Museum Meanings) Boulder, Co. netLibrary c2001-c2003
- Poli, C. Mobility and Environment: Humanists versus Engineers in Urban Policy and Professional Education. Dordrecht; New York, Springer c2011

Researching Distributed Currencies no comments
Researching Distributed Currencies.
Over the course of my time here studying Web Science, I would like to do some in depth research into distributed currencies. A distributed currency is a form of money with no centralized processor or controlling authority. At the moment there are only a handful of distributed currencies in existence, and the majority of them stem from Bitcoin. Bitcoin is a “totally” anonymous and distributed online currency. It’s similar to PayPal in that you can use it to buy things online and send/receive currency quickly and conveniently.
PayPal is the opposite of a distributed currency, it’s centralized. PayPal handle all the processing of transactions, and they are also the authority for all transactions and for this service they charge a small fee on each transaction (varying from 2% – 8% of a transaction + a fixed 20p.) If PayPal doesn’t like a transaction, it will slow it, stop it or outright take your money away (googling PayPal took my money returns over 6million results.)
A distributed currency is not centralized. The transaction processing is handled by anybody who chooses to use the currency which normally involves running some client software. Because it’s running on anybodies computer, the currency must be designed in a secure way that doesn’t allow individual clients to tamper with or reverse transactions. The implications of this are a totally unregulated currency where nobody can decide what is right or wrong.
The pro’s of this are that people can make transactions for anything they want, without the worry of their account being frozen or their transaction being blocked or slowed or outright refused by a regulatory authority like PayPal. There is no single point of failure (or corruption.) Also, there is no mandatory fee’s to use these currencies or make transactions. The open distributed nature utilizes the internet in the way it was intended. It could be argued that centralized services governed by one authority undermine the entire point of have the internet (a distributed network) in the first place.
Bitcoin is totally anonymous also. If you want to receive money, you give someone a wallet address. You can have as many wallet addresses as you want which has the end result of it being impossible to link transactions to people. However, combine anonymity, money, and no regulation or authority and sure enough, you get criminals.
Bitcoin received a lot of publicity after the launch of a website called silkroad which was described as “the Amazon marketplace of drugs” which allowed users to by all sorts of illegal items including drugs and weapons – all paid for by the anonymous distributed currency Bitcoin. As well as Silk Road for weapons and drugs, there have also been suggestions that Bitcoin is used to trade in other illicit things such as hiring bot nets, hitmen, slaves, prostitutes and more.
Because there are supposedly a large amount of criminals using Bitcoin, there is a lot of fraud. Browsing Bitcoin forums and it’s not hard to find posts of people frustrated at being scammed out of several hundred Bitcoins (the current conversion is 1btc = $3) because there is no regulatory authority to reverse fraudulent transactions.
However, that’s not to say everyone that uses Bitcoin is a criminal or that every transaction is related to an illegal item. The idea of totally free online transactions should appeal to anybody that sells online, as it could result in lower product prices for the end user.
Over the course of my research, 1 of the many aspects of distributed currencies I would like to look into is ways of making a distributed economy that is less risky to use (e.g. reducing fraud and scams, it maybe that this means reducing anonymity) but maintaining the benefits of free transactions and no single point of failure/corruption.
My 2 subjects of research
My background is in computing science, I think it would be useful for me to also have a better understanding of economics and and criminology for the aspect of research above. Why?:
Economics: wikipedia described economics as “the social science that analyses the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.” I believe a deeper understanding of this and the methods associated with economics would allow me to conduct more informed, appropriate and educated research and to account for and explain the necessity of currency, trade and economies. Specifically I would like to look into online/cyber economics as it’s important to understand the differences (if any) between how people trade online vs. in the real world and how to cater towards these differences and incorporate them into my future research.
Reading Material
I’m not sure yet, I’ve been looking for economics books relating to the web and internet but have been unsuccessful in finding any so far. If anyone has any suggestions, please don’t hesitate to put them forward!
Criminology: wikipedia describes criminology as “the scientific study of the nature extent, causes and control of criminal behaviour in both the individual and in society.” In order to protect something against crime and fraud, I believe it’s important to first understand why people commit crime and fraud in the first place. Specifically I would like to look into cyber criminology to try and get an idea of the research methods used to access and understand such a dark corner of the web. I’d like to learn if and how researchers in this area get full, truthful and honest answers from an area that is inherently full of people willing to mislead.
Reading Material
Not 100% sure on this one yet, but here’s a few ideas:
Cyber Criminology: Exploring Internet Crimes and Criminal Behaviour (2011)
http://www.crcpress.com/product/isbn/9781439829493
“Approaching the topic from a social science perspective, the book explores methods for determining the causes of computer crime.”
Cyber Forensics and Cyber Crime: An Introduction (2008)
http://www.amazon.com/Computer-Forensics-Cyber-Crime-Introduction/dp/0132447495/
“It includes and exhaustive discussion of legal and social issues, fully defines computer crime…provides a comprehensive analysis of current case law, constitutional challenges and government legislation”
01 – Museum collaboration. no comments
How can smaller museums have access to exhibition artifacts?

Main Concept
I believe that museums should be able to collaborate with other museums. Not only in their same country but also around the world. The Museums Association (MA), along with The Museums, Libraries & Archives Council (MLA) in the UK, indicates that a museum should “enable people to explore collections for inspiration, learning and enjoyment.”
This means that the cultural motivation or agenda of the museum can be manipulated by different factors like: political, economical, location, etc…
The different agenda that the museum can follow, motivates me to approach the problem from different perspectives and disciplines.
The main two disciplines
Within Web Science, my main two disciplines will be:
- Museum Studies / Museology
- Information Technology for Organizations
Museum Studies
Through the museum studies, I will be attempting to explore the different museum methodologies but focusing mainly on the purposes of the museums and how the response from people. Peter Vergo mentioned in 1989
… too much about museum methods and too little about the purpose of the museum …
(Vergo, 1989: 3)
This indicates how it is not only important the methodological approach wich is directly related to Graphic Design and Visual Communication; which is my area of expertise.
The MLA indicates a basic typology of museums that can be able to target the different approach for the museum purpose within the UK.
- National museums
- Local authority museums
- University museums
- English Heritage museums
- Independent museums
- National Trust properties
- Regimental museums and armouries
- Unoccupied royal palaces
Being a Web Science research, this typology will have to be challenged and extended in order to globalize the museum typology throughout the world.
Through my research I will attempt to develop a new approach of how museums exhibit to their public by extending their exhibition material through different collaborative processes.
Information Technology for Organizations
Within the IT for Organizations, the technology developed can be able to adapted for the requirements of the institution or organization. Through this discipline I believe I can target a different problematic of museum collaboration. Issues like: e-learning, disabled IT access, gaming, security system, etc..
A full technological approach with a sociological combination will allow the research to preview different areas of improvement. Areas in which museums, institutions and academics can be able to benefit from it.
My next step
Throughout the next days I will start to gather the essential bibliography for this research. I will start posting the main theories and methods gathered from these books and start finding people that relate or can be able to collaborate with my research. Ultimately I will like to find some institutions that are keen is promoting these kind of ideas to provide support to smaller museums that are struggling to get ‘out there’.