Archive for the ‘Identity’ tag
Philosophy and Identity – Here I go . . . no comments
To start with I am going to look at what Philosophy thinks identity means. This was a slightly naive aspiration as this is a fairly large area of philosophy. Below I have put some notes of the progress I have made so far.
Identity is not a simple question in philosophy. There are several theories surrounding the issue of “who am I?”.
Dualism (Maslin, 2001)
- Humans are composed of 2 entities: non-physical soul/mind and the physical body
- The “person” is the consciousness or the entity that experiences and it is identical to the soul but does not include the body
Identity Theories (Reductionism)
Part of philosophy investigates the concept of mind and body, mind-body problem. What is the body? Who does it belong to? What is the mind? Is it the brain or is it something more? (Mullen, 1977).
Mind/Brain Identity Theory (MBIT)
- MBIT denies Dualism
- Mind is not separate from the brain
- everything is physical, including consciousness and thoughts => exemplifies Materialism
MBIT defines a “brain event” as the living brain and the mental events. Identity theorists explain that mental states are brain states. However, this isn’t a bi-directional relationship. I understand it in terms of
Mind = Brain Events BUT NOT Mind ≡ Brain Events
So to explain this in terms of maths:
x + 3 = 5
In my example:
x = 2
However 2 will NOT always equal to x.
So when identity theorists refer to Mind and Brain events, it is not correct to interchange the terms whilst describing one side of the relationship. These theorists are not proposing an Analytical Reduction relationship like the following statement “All trilateral are identical with three-sided figures”. As trilateral means three-sided figure, this statement is always analytically true – it can never be false. (Maslin, 2001)
Identity Theory can be further broken down into the following theories:
Terms:
Example – “love and love and love”
Token = 5 “Token” Words
Type = 2 Types
- love
- and
Types are a broad class which categorises a number of tokens.
Token-token Identity Theory (Maslin, 2001)
- mental tokens are just physical events (e.g. occurring in the brain)
- Every token of mental state could be identical with token type of physical state but that mental state will not always generate the same brain state, at a different point in time.
Type-type Identity Theory (Maslin, 2001)
Water = H2O
Lightning = Pattern of Electrical Discharge
The contents on the right explain the hidden nature of the left-hand items. All lightning flashes will always be patterns of electrical charge but not all electrical charges will be lightning.
Mental State => Brain State
The Brain State for a particular Mental State will have to be observed, can’t just be predicted.
Other
Identity through labels (Mullen, 1977) – haven’t quite figured out the term for this
Someone can be labelled as:
- a father
- son of . . .
- brother of . . .
- owner of a golden retriever
- CEO of Google
Is our identity defined by the labels placed on us by those around us? If this is the case, does our identity depend upon those around us?
Do these different labels/roles result in different behaviours and acceptable personas. What does this mean for our identity on the web? Some argue each label/role has an accepted scope of behaviours linked to it. When we accept the label we accept these conditions of behaviour for the period of time that we are still defined by that label.
Semantic Web – How will all these personas appear in a semantic web where you are represented by one URI? Sometimes different areas of your life shouldn’t interact e.g. photographs of a young working professional out drinking on a Friday night and a primary school head teacher as these are different segments of this persons life.
Bibliography
Maslin, K.T., 2001. An Introduction to the Philosophy of Mind. Polity ; Blackwell Publishers, Cambridge, UK : Malden, MA.
Mullen, P., 1977. Beginning Philosophy. Edward Arnold, London.
http://forums.philosophyforums.com/threads/typetype-vs-tokentoken-identity-15036.html
Initial Thoughts – Problem and Disciplines 1 comment
I am very interested in the issues of identity within the Semantic Web and Linked Data. Moving from a web of documents to a web of data with URIs (unique resource identifiers) for every referenced object/thing/person, aims to create new links between related content. However what happens when you want to refer to a person or thing which isn’t already referenced? This new object will be assigned a URI and others will then be able to link to it. However, who will manage this data and ensure it is correct? This issue is especially significant when referring to an individual. If someone has no intention of creating an online presence or doesn’t have access to the World Wide Web, what impact will this URI about them have on their life? They might not even be aware that a whole series of connected data about them is being collated on the web for everyone else to access. I am going to look at this area from the point of view of philosophy and either sociology or anthropology.
I have started my research by looking into the recognised strands of each of these disciplines.
Philosophy contains a number of interesting areas which could be applied to this problem. Philosophy of language could look at how the use of language could affect the formation of an online network and linked data, (http://www.philosophy-index.com/philosophy/language/). The political angle of philosophy would be interested in government, law and social justice, (http://www.philosophy-index.com/philosophy/political/). But possibly the most interesting angle would be to look at the philosophy of the mind, specifically the mind body problem (http://www.philosophy-index.com/philosophy/mind/mind-body.php). This train of thought would look at the idea of mind and body being separate and a philosopher could argue that each should have their own URI?
Secondly I want to look at the idea of URIs and identity in relation to cultures and at the societal impact that online identity could have. Sociology could include the social organisation or social change (http://savior.hubpages.com/hub/Areas-of-Sociology).
Similarly to Philosophy, Anthropology could include the study of language, and how this could impact the online community. Linguistic Anthropology looks at the cultural impact on nonverbal communication (http://anthro.palomar.edu/intro/fields.htm). Cultural Anthropology:
“All of the completely isolated societies of the past have long since been drawn into the global economy and heavily influenced by the dominant cultures of the large nations. As a consequence, it is likely that 3/4 of the languages in the world today will become extinct as spoken languages by the end of the 21st century. Many other cultural traditions will be lost as well. Cultural and linguistic anthropologists have worked diligently to study and understand this diversity that is being lost.” (http://anthro.palomar.edu/intro/fields.htm).
This field might look more negatively upon the web, as a tool which is potentially destroying the traditions and cultural diversity, which makes the world so varied.
This is a very brief introduction to the problem and fields which I wish to investigate.
Who am I? no comments
This week I have been reading around the subject of self and identity, which is concerned with how the everyday concept of self has been theorised in social psychology.
Social cognitive models describe self as a piece of knowledge and considers how particular kinds of self representation are assessed in different situations. There seems to be a lengthy discussion on the ideal and the ought self as opposed to the actual self. Discrepancies between the ideal and the actual or the ought and the actual are said to be responsible for the positive or negative effects on self-esteem. The plan is that people have for achieving this eternity of cells in the future, as well stay current discrepancies from them, are considered to be important contributors to people’s experience of themselves in the present. In addition, it is noted that people engage in processes of self-evaluation and self regulation, the assessment of how one is doing compared to others, and intentional efforts to modify aspects of one’s self. All these models have something to do with the ways in which the knowledge that people have about themselves becomes a relevant in particular circumstances, and how these guides are their behaviour accordingly.
On the other hand, social identity as a contrasting model considers how the social groups of which we are members impact on our sense of self. According to this model, all experiences in children live Kurds continuously from interpersonal to intergroup interaction. It is believed that there is the further we move towards the intergroup situation, the more depersonalise our sense of self becomes. In other words, we begin to think of ourselves more and more in terms of those characteristics that we share with other group members. This in turn is closely linked to personal attitudes and perception of group identity.
This new model has led to further research into ways that people share representations of self within the groups. In particular, they consider the ways in which socially shared representations of the self and of the social groups that contribute to one’s sense of identity shape the context within which people develop their self concepts. Of course, individuals may differ in the extent to which elements of particular social representations are incorporated into their self concepts, the importance of social representations in forming a shorter and vermin surrounding these selves means that social representations cannot be reduced to individual difference variables.
Finally, I have touched on the work of social constructionist. Some seem to believe that the conditions of contemporary life are undermining the notion of an integrated and stable self. However, others have also argued that the constructed the nature of the self is being reviewed in the ordinary experiences of everyday life, and is provoking the prices as the ontological basis of cells apparently unravels. Therefore, the challenge for people in this world is to construct a sense of identity which does not require the self to be a faithful reflection of inner capacities and qualities but which, rather, sees the self as a constructed achievement of relational social life.
Moving on
This is my last reading based post on this blog. In view of the time left, my next blog will focus on summarising and recollecting what I have learned so far, and will begin to move towards a synthesis version of all the information presented. In particular, these will be discussed or analysed in relation to E learning.
Identity (Post 5 – More Anthropological Views) no comments
This post will hopefully conclude the final underlying principles and theories of Anthropology, as described in Small Places, Large Issues. These latest concepts have centred on social systems and social structures, with the two being distinguished as:
- Social Systems: Sets of relationships between actors;
- Social Structures: The totality of standardised relationships in a society.
This definition of social systems relates to social networks – the relationships from a particular person, and the scale of these networks has to be considered in contemporary Anthropology as the Internet has meant that non-localised networks are of increasing importance compared to the traditionally studied small-scale societies. Rather than simply focusing on online research to study these networks, however, anthropology stresses an importance of collecting other forms of data: specifically on relationships between online activities, and other, offline, social activities. By doing this, it has been shown that the Internet/Web can surprisingly enhance people’s national and even religious identity, with the example of Trinidadians whose offline and online activities form a single entity – their identity does not seem to be being altered by the Web.
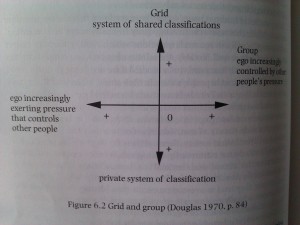
Grid and Group Classification of Societies - from "Small Places, Large Issues: An Introduction to Social and Cultural Anthropology" Second Edition, by Thomas Hylland Eriksen, page 82.
The above image displays a classification system for societies that focuses on social control. The “Group” axis classifies societies according to their social cohesion, and “Grid” on the shared knowledge in a society. A strong grid, strong group society is explained as a strictly conformist society where an individual’s identity is constructed through the public system of rights and duties. The measures on this grid can help to explain how the identity of individuals in certain societies is shaped through the social control exerted by the social system itself. A typical industrial society could fall in the weak group, weak grid sector (although they can be spread out over the graph), where members are “individualistic and anonymous, and thus others exert little social control over ego” (page 83). A counter argument is that the influence of the state on a society means that they should fall into “Strong group”, so the variation in opinions here is vast and the classifications all seem uncertain and unreliable. It appears to have more value when classifying one particular society, rather than a group such as “industrial society” which is far too vague.
There are differing schools of thought that cover the link between society and individual actors:
- Individualist thought, associated with Max Weber where anthropologists try to find out what makes people do what they do
- Collectivist thought, associated with Marx and Durkhein where anthropologists are more concerned with how society works.
Theories that focus on the actor emerged to critique structural-functionalist models in the 1950s. In these models, the individual was mainly looked over, with focus instead on social institutions. This was criticised, as it was not clear how a society could have needs and aims, and because society can only exist because of interaction – this implies that social norms must be seen as a result of interaction, and not the cause. The author summarises by stating that while structural functionalism seeks to explain cultural variation, it only succeeds in describing interrelationships.
Finally, it is described how Bourdieu examined the relationship between reflexivity or self-consciousness, action and society, resulting in a theory of “culturally conditioned agency”. “Habitus” is the term used by Bourdieu to describe “embodied culture” which enforces limitations on thought when choosing an action, and ensures that “the socially constructed world appears as natural” (page 91). This raises the question of how much of what we do and who we are is just down to habits, conventions and norms imposed on us by the society we are born in to?
As the subject matter of the book is now beginning to move away from the core anthropological theories and on to more specialised areas I will start to focus my reading on specific chapters relating to Identity to build up my knowledge of this area, before moving onto some introductory psychology texts.
Identity (Post 4 – Socialisation) no comments
Following this week’s session on the blogs, I think I probably need to focus more on the discipline, rather than the issue whilst summarising my reading. I have continued reading through Small Places, Large Issues to help further my understanding of Anthropology, although the chapters I am covering now are all relevant to my chosen issue of Identity.
The book describes a slight change in Anthropological research in recent times, with the majority of material collected in the past coming from in-depth ethnographical studies of local communities. However it has become common now that additional sources other than fieldwork now contribute to the research, including historical sources and the media. The main focus of the study remains on the “interrelationships between different aspects of social and symbolic systems through participant observation”, although there has been a movement away from the traditional focus on isolated villages in remote parts of the world. Local communities are said to have traditionally been the focus of studies due to them being “methodologically manageable units”, where participant observation is easy, and the anthropologist can become familiar with each individual and their relationships with each other. However, there is an increase in focus on larger social systems with unclear boundaries, but the techniques and theories used to study these are generally similar, supplemented by more methods other than participant observation.
My last post covered a section of the book focusing on people as individuals and their statuses and roles within particular contexts. My latest reading has covered the social life from the perspective of society. Socialisation – “the process whereby one becomes a fully competent member of society” is something that seems interesting, with many anthropological studies showing that child-raising is linked to the shaping of behaviour and thoughts in a society’s members. The concept of Anomie (Durkheim) where one becomes alienated by an inability to match the values of society has been shown to exist in many societies, even where the society is tightly integrated. Anthropological studies can also examine the traditions associated with how one’s identity changes over time, with members of a society transitioning from one stage of their life to the next through a rite of passage. The book suggest that the question of whether we are ‘the same person’ throughout our lives is a philosophical issue, with anthropology seeming to suggest that this is not so. It will be interesting to see the psychological perspective on this issue.
Identity (Post 3 – Statuses and Roles, and an Anthropological view on the Self) no comments
This week I have continued reading Small Places, Large Issues by Thomas Hylland Eriksen. After covering the introductory sections as last week, I wondered whether to skip forward to the chapters later in the book that the index points to for ‘Identity’, or to continue linearly from the beginning. After quickly skimming through the upcoming chapter, it seemed there was a lot of relevant material, so I continued on as before.
Titled “The Social Person” I had a feeling that this chapter could contain a lot of material that could be linked to Identity. Indeed one of the first issues covered is that of the different dimensions of human existence. These are divided into four categories in the following way:
Culture: Cultural Universals Cultural Variation
Nature: Genetic Universals Genetic Differences
The bottom two sections cover biological features in humans, which do not feature much in anthropologic research. However, the top sections are important and fundamental to anthropology, as there is much variation between humans that cannot be accounted for through genetic variation.
The next big point made is regarding language, and how although it is sometimes assumed that language is uniform across a whole group, it can be found that there is as much linguistic variation within the group.
The book then goes on to describe statuses and roles that account for the rights and duties that an individual may hold in relation to others, and which can vary depending on the situation. The example used to explain this is that of a bus driver, the driver’s status is ‘Bus Driver’, whereas his role is defined by what one does as a bus driver. The work of Goffman (1978 [1959]) is referenced in order to explain how one may switch between roles using “impression management” to appear a specific way in a certain situation. It is then stated that Goffman’s main idea is that social conventions define everything an individual does as a “social creature”. Everything one does follows culturally or socially defined rules.
One area that I read about last week, and didn’t include in my post is the distinction between a view from the inside of a culture, and the view from the outside. Two terms are used for this: emic and etic. Emic describes life as a member of a particular society experiences it, whereas the etic level is the analytical description of a researcher after observing a society. Taking this into account, Goffman’s role theory is an etic explanation as it as an abstraction of the processes of social life.
I was interested to read the next section, which moved on to talking about the Self. A distinction is made between the public and private self, with the “I” being the private self as seen from the inside, which isn’t easily assessed by anthropologists. This is something which I am certain will be covered when I begin to tackle Psychology, and will be an important area to compare and contrast the two disciplines. I am glad I decided to continue reading linearly, as with no reference to this section under Identity in the index I may well have missed it, although the concepts of the Self seem central to the issue of Identity. Maybe I am mistaken, and this will be cleared up once I read the main Identity section.
The biggest idea I took away from this section on the Self is the work of Brian Morris (1994) who distinguished three areas of personhood. Firstly, a person may be identified as a conscious and social human being, and is something which seems to be universal. Secondly, a person may be categorised as a cultural category, which the author explains may be more or less inclusive than the first point – some societies will exclude strangers for example from full personhood, but in others it may be that “non-human” entities may be included. Finally, there is the “I as opposed to others” component, which, depending on the culture, is interpreted differently.
Having advanced further into the realms of anthropology, I then decided to take another anthropology book, this time Cultural Anthropology: A Contemporary Perspective by Roger M. Keesing and Andrew J. Strathern, and skim through the opening few chapters. My reason for this was to ensure that I had covered the same basic points relating to anthropology. Familiar topics such as the difficulty in defining culture, ethnocentrism, ethnography and social roles all appeared, giving me a fairly good boost of confidence that makes me think I’m heading in the right direction with anthropology.
Identity (Post 2 – Basic Anthropology) no comments
My reading this week has focused on gaining a basic understanding of some of the underlying concepts on anthropology, before I turn to look at Identity from this point of view. I have started by reading “Small Places, Large Issues: An Introduction to Social and Cultural Anthropology” by Thomas Hylland Eriksen, from which some of the elementary points I have gained are described below.
One of the primary issues described immediately is that of ethnocentrism which occurs when a researcher examines a subject from only the point of view of their own background, and will therefore only describe it from their own culture’s perspective. This can lead to the researcher believing that their own cultural group may be superior to the group which they are researching, as they are only looking at it in comparison to what they are familiar with (pages 6-7). In contrast to this, cultural realism would state that “Cultures are qualitatively different and have their own unique inner logic”, and that ranking can not be used to distinguish different societies. Ultimately, cultural realism would believe that as long as something makes sense in a particular context, then it is as good as everything else, and it is not likely that this is followed by anyone completely outside of their line of work (page 7).
The book then began to cover a brief overview of the history of anthropology, and one concept immediately struck me as having relevance towards Identity, but according to the book it has never been part of the mainstream anthropological thinking outside of Germany. Diffusionism, “the doctrine of the historical diffusion of cultural traits”, seems to have been left behind after the First World War when studies on societies where taken without looking into the historical development of those societies (page 13). In terms of Identity, I believe there must be something in this area about the historical basis of a culture’s identity, so it is something I will investigate – the globalisation theory is reminiscent of diffusionism and “attempts to understand the ways in which modern mass communications, migration, capitalism and other ‘global’ phenomena interact with local conditions” and will also be worth looking at.
The final concept I will cover in this post is ethnography, which aims to develop a thorough understanding of the culture or society being investigated (page 24). It is the fundamental research gathering technique used by anthropology, and is generally where differences can be drawn with other social sciences as the study will generally cover a long period of time. The author uses a good analogy to differentiate anthropological views and historical views: “Anthropology may be described as the process whereby one wades into a river and explores it as it flows by, whereas historians are forced to study the dry riverbed.” However it is stressed that the two should not be seen as mutually exclusive, throwing weight behind my theory that looking at diffusionism may be of value in this study (page 33).
Now that I have at least some understanding of the basic concepts behind anthropology, I will this week begin to look a bit more at how Identity is seen from this discipline, and what other areas of the subject I will need to look at.
Identity no comments
I have chosen Identity as my issue to study, and will examine this from a psychological and (socio-cultural) anthropological perspective. I am interested in the effect that the Web can have on different cultures and different people, so I think these two disciplines fit nicely with that interest and will hopefully build up a solid background in part of a wide area that I am keen on studying for my dissertation. The two disciplines should allow me to contrast what psychology says about the identity of the individual, with the theories of anthropology regarding the formation of cultural identity.
I will begin by reading the basic textbooks in each area:
- Handbook of Self and Identity by Leary, M and Tangney, P
- The Self by Sedikides, C
- Cultural Anthropology A Contemporary Perspective by Keesing, R and Strathern, A
- Small places, large issues : an introduction to social and cultural anthropology by Eriksen, T
Hopefully these will be a good start and direct me to other important books in this area!