Summary
Harmonics
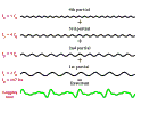
Musical notes are complex tones consisting of a fundamental frequency, f, and higher harmonics (or partials) that are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency (2f, 3f, 4f,…). The pitch of a note remains unchanged even if its fundamental frequency as well as its first partials are removed.
Shepard/Risset tones

These paradoxical notes seem to keep rising for ever.
Beats
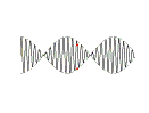
When two pure tones of very similar frequency are played together they produce beats at a frequency equal to the difference between the original two frequencies.
The sound of filtering
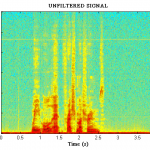
Filters can remove certain frequency bands and leave others unchanged.
Sum and difference tones
When two tones are played together at sufficient volume the ear hears a fictitious difference frequency.