Archive for the ‘Uncategorized’ Category
Demographic World View: Act One Scene Two no comments
Etymologically, demography comes from the Greek words demos (for population) and graphia (for description or writing).Demography stated informally tries to answer the following questions:
– How many people of what kind are where?
– How did the number of people come about?
– What is the implication of the number derived?
Formally, demography is the scientific study of human population and its dynamics.
Demography deals with aggregates of individuals, it describes the characteristics of population. Most demographic studies employ quantitative and statistical methods, features of population are often measured by counting people in the whole population or sub-populations and comparing the counts.
Population size is a number with absolute and relative connotations. In the absolute sense, human population size quantifies the number of people in a country, region or space. Beyond the numerical quantity is the concern for distribution both within and among country, region, or space, this accounts for the relative connotation. Resulting from the concepts of population size and distribution is population density which is the relationship between population size, distribution, and the space that contains it.
Population density is consequential to the well being of the population. Notably, population density explains the viral spread of disease, knowledge, and ideas; epidemics is most likely to occur in a densely populated space as knowledge and ideas can easily diffuse.
Population study is concerned with the size and distribution of identifiable subgroups within populations. This concern yields information on the structure and composition of population. The characterization (categorization or classification) of population relies on endless list of traits- age, gender, education, religion, income, occupation, language, race, ethnicity etc. However, some traits are more useful; traits that change less frequently or has predictable pattern of change. Age and gender are the basic and most influential characteristics to demographic processes, hence they are known as demographic characteristics.
The dynamics of population is rooted in the basic demographic processes of birth, death, and migration. Basically, population changes can be associated with leaving or entering; to leave means dying or emigrating and to enter means being born or immigrating. This fact can be depicted in the basic demographic equation that follows:
Pt+1 = Pt + Bt ,t +1 – Dt ,t +1 + It ,t+1 – Et ,t+1
where Pt is the number of persons at time t and the number of persons one year later is Pt ,t+1; Bt ,t+1 and Dt ,t+1 are the number of births and deaths that occur between times t and t+1 respectively; It ,t+1 and Et ,t+1 represent the number of immigrants to and emigrants from the population respectively between times t and t+1.
The difference between Bt ,t+1 and Dt ,t+1 is referred to as natural increase (or decrease when the difference is negative) while the difference between It ,t+1 and Et ,t+1 is known as positive net international migration when the difference is positive and negative net international migration otherwise.
Growth in demographic parlance refers to change in population size. From the demographic equation above, growth means the difference between Pt+1 and Pt even though this difference is negative. The interplay of demographic processes results in population growth as well as compositional changes in population.
Readings
David Yaukey and Douglas L. Anderton, Demography: The Study of Human Population 2nd ed., 2001
Dudley L. Poston, JR. and Leon F. Bouvier, Population and Society: An Introduction to Demography, 2010
Current disciplinary debates in Political Science no comments
Political Science
The book I have been reading this week contains an overview of how political science has evolved in the last decades as a discipline. Entitled Making Political Science Matter (Schram & Caterino, 2006), this edited book builds up on a debate sparked by Flyvbjerg (2001) focused on the limitations of current methodologies –current at that time- in social inquiry. One of the book’s claims is that methodological diversity in this field is somewhat constrained by the pluralism of post-positivism. In other words, positivism in political sciences emulates natural sciences in dividing the discipline in subfields that become isolated one another, each one with their own methodologies. Owing to this division or constrained pluralism, a need of ‘trading zones’ or common understanding between disciplines has been identified.
Also, all essays in the book are highly critical to the application of ‘hard science’ -in which quantitative methods are included-, in political analysis, as this approach seems to be too distant to the object of study, which in this case is the society, composed in turn by people, not objects. This is why hard science cannot fully explain or provide a complete understanding of social phenomena. This limitation is leading to a revolutionary period in which a movement called Perestroika is challenging the current paradigm in social science. Together with Flyvbjerg, Perestroika aims to include –not to switch to- phronesis in the study of politics. Phronesis is a key term in the flyvbjerian debate, meaning that intuition and practical wisdom are critical to the study of social phenomena.
In short, from this book, it seems like political science is distancing from the paradigms of natural sciences, moving towards an approach in which social and political phenomena are approached from a more humanist perspective, in which personal experience gains significance. This shift might be necessary to be considered by other disciplines such as computer science when looking for a common ground , a ‘trade zone’ in which to have a fluid communication.
Introductions: Risk Management no comments
Last week I was very excited to take a look at technoethics and found that the more I read, the more I wanted to read about it. This week, reading around the area of risk management, I have found myself in a similar situation. My mind has been buzzing with ideas about how these fields can contribute in a big way to Web science. Nonetheless, I will briefly introduce the area of risk management at this time and share these potential applications in my future posts.
Brief Overview of Risk

Defining Risk
Before talking about managing risks, it is fitting that I define risk. It has been noted that risk is defined differently from one field to the next and there is sometimes contradiction in its definition (Vaughan, 1997). This lack of agreement on definition has been partly attributed to the relatively young age of the field and practitioners adopting definitions of risk from varying fields. However, for the purposes of my adventure in the discipline, I have chosen to define risk as “an event with the ability to impact (inhibit, enhance or cause doubt about) the mission, strategy, projects, routine operations, objectives, core processes, key dependencies and or the delivery of stakeholder expectations.” (Hopkin, 2010, p. 12).
When an organisation employs the Web, it is hoped that it will lead to a favourable outcome (e.g., increased productivity) and not hurt the company (e.g., cause legal troubles) in any way. In many situations within organisations, especially when technology is involved, the result could be uncertain and this constitutes a risk. For example, as the impact of the Web could be different to what is expected, its adoption could be considered as being a control risk.
Types of Risk
There are several ways to classify types of risks and there appears to be no generally accepted classification that is right or wrong. Practitioners often adopt classifications that are appropriate for their circumstances. In addition to the control/uncertainty risks mentioned, texts usually mention two other risks: hazard/pure risks and opportunity/speculative risks. Hazard or pure risks typically refer to things like theft, health and safety risks. Opportunity or speculative risks are usually associated with financial investments, critical business decisions such as moving location or offering a new product, and also, taking or not taking the opportunity.
Not All Risks Are Equal
As you can appreciate, some situations pose a higher degree of risk than others. Situations where there is a high likelihood of a negative outcome occurring or a high probability of loss are usually considered as being riskier than situations at the other end of the spectrum. A good example of this is given by Vaughan (1997). When playing Russian roulette, there is more risk with each bullet loaded into the gun, (until obviously when the barrel is fully loaded – it’ll be certain you’re going to get shot).
Brief Overview of Risk Management

Defining Risk Management
Hubbard (2009) defined risk management as “the identification, assessment, and prioriti[s]ation of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimi[s]e, monitor, and control the probability and/or impact of unfortunate events” (p. 10). Simply put, Hubbard believes risk management is “being smart about taking chances.” Having looked at many definitions, one consistent and important characteristic of risk management is that it is a systematic approach to dealing with risk that follows a particular process depending on the risk circumstance.
Some texts (e.g., Scarff, Carty & Charette, 1993) has found it necessary to separate the concepts of ‘management of risk’ and ‘risk management’. The latter refers to the activities of planning, controlling and monitoring, whereas the former includes such activities, as well as those associated with risk analysis.

Dealing with Risk
Risk management aims to eliminate, reduce or control risks and gain enhanced usefulness or benefits from them (Waring & Glendon, 1998). It has been suggested that successful risk management programmes feature a strategy that is:
- proportionate to the level of risk posed;
- aligned with other business activities;
- comprehensive, systematic and structured;
- embedded within business processes;
- dynamic, iterative and responsive to change.
According to Waring and Glendon (1998, p. 9), risk management involves the optimal combination of the following strategic options:
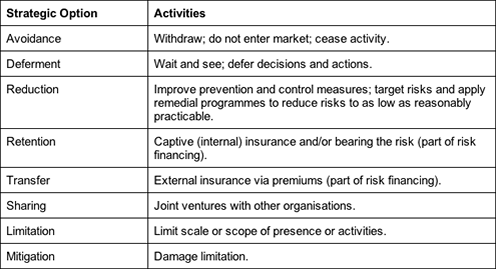
Notes
This Week’s Plan
- Reading more about the methodologies associated with the selected disciplines.
- Prepare a blog post that describes the methodologies adopted by the selected disciplines and compare them.
- Explore the contributions these disciplines could make to each other and Web science.
- Publish a blog post that discusses the potential applications of these disciplines to Web science.
Last & Previous Week’s Plan
Identifying the simplest books to read that will give an easy to understand introduction to the disciplines I picked.Making notes on books read.Prepare a blog post that gives an overview of what I want to work on.Publish a blog post that introduces technoethics.Publish a blog post that introduces risk management.Outline a reading plan for moving forward.
Introductory Readings
Ethics: A Very Short Introduction– Simon BlackburnHandbook fo Research on Technoethics– Rocci Luppicini & Rebecca AdellManaging Risk: Critical Issues for Survival and Success Into the 21st Century– Alan Waring and A. Ian GlendonIntroduction to the Management of Risks– Frances Scarff, Andy Carty and Robert CharetteRisk Management– Emmett J. VaughanThe Failure of Risk Management: Why It’s Broken and How to Fix It– Douglas W. HubbardFundamentals of Risk Management Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Risk Management– Paul Hopkin
Marketing Management Philosophies – New Economy – Information Bussinesses no comments
Marketing is a social and manager process whereby individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and values with others. There are five alternative concepts under which organisations conduct their activities, the so-called marketing management philosophies: the production, product, selling, marketing and societal concepts. The production concept holds that consumers favour products that are available and highly affordable; management’s task is to improve production efficiency and bring down prices. The product concept holds that consumers favour products that offer the most in quality, performance and innovative features; thus, little promotional effort is required. The selling concept holds that consumers will not buy enough of the organisation’s products unless it undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort. The societal marketing concept holds that generating customer satisfaction and long-run societal well-being are the keys to both achieving the company’s goals and fulfilling its responsibilities.
Most successful and well-known companies have adopted the marketing concept, according to which achieving organisational goals depends on determining the needs and wants of target markets and delivering the desired satisfaction more effectively and efficiently than competitors do. Implementing the marketing concept often means more than simply responding to customers’ stated desires and obvious needs. Customer-driven companies research customers to learn about their desires, gather new product and service ideas, and test proposed product improvements.
The explosive growth in connecting technologies has created a New Economy which provides marketers with new ways to learn about and track customers as well as create product and services tailored to meet customer’s needs. Marketers have redefined how they connect with their customers; in contrast with yesterday’s companies that focused on mass markets, today’s companies are selecting their customers more carefully and developing more lasting and direct relationships with them. Web seems to enable customer relationship building as companies can demonstrate the abovementioned marketing concept on their web sites by including features that are important to consumers; online companies have moved from mass marketing to segmented marketing or one-to-one marketing, in which they target carefully chosen individual buyers.
The New Economy revolves around information businesses; information has the advantages of being easy to differentiate, customize, personalise and dispatch at incredible speeds over networks. With rapid advances in connecting technologies companies have grown skilled in gathering information about individual customers and more adept at individualising their products. Marketing companies go to great lengths to learn about and understand their customers’ needs, wants and demands; they build extensive customer databases containing rich information on individual customer preferences and purchases and then they mine these databases to gain insight by which they ‘mass-customise’ their offerings to deliver greater value to individual buyers. Web enables consumers and companies to access and share an unprecedented amount of information with just a few mouse clicks. In order to be competitive in today’s new marketplace, companies should adopt web technologies or risk being left behind.
**************
Armstrong, G. & Kotler, P. (2003) Marketing: An Introduction. New Jersey: Pearson Education Ltd
Drummond, G. & Ensor, J. (2005) Introduction to Marketing Concepts. Oxford: Elsevier Butterworth – Heineman
Kotler, P., Armstrong, G., Saunders, J., Wong, V. (2001) Principles of Marketing. New Jersey: Pearson Education Ltd
Palmer, A. (2012) Introduction to Marketing: Theory and Practice. Oxford University Press
Masterson, R. & Pickton, D. (2010) Marketing: An Introduction. London: SAGE Publication Ltd
Introductions: Technoethics no comments
Moor on Ethics & Technology
Moor (2005) believed that with an increase in the social impact of technological advances, the number of ethical challenges also increase. He suggested that this is a result of the ever-increasing novel uses of technological advances and a lack of ethical inquiry into these activities. For example, the Web has fundamentally altered the social contexts within which we live, work and play. It has raised several questions including some about the legitimacy of human relationships maintained using its platform, its facilitation of illegal activity on a large scale and the privacy of its users.
However, though these are very present and pressing societal issues, they are also vast areas for investigation, and there is relatively sparse research coverage. Also, an added dimension to this challenge is that technological advances seem to continuously change the standard ethical questions. Thereby researchers are forced to simultaneously attempt to explore the ethical implications of these technologies as they were, are now and could be in the future.
Technoethics: Tackling New Types of Ethical Questions
Unsurprisingly, many of the current debates surrounding technological advancement are addressed by technoethics (TE). They are some of the most challenging issues that scientists, innovators and technologists will face. These challenges usually characterise the roles these individuals play when plotting an ambitious route for the future. They inadvertently raise important questions about rights, privacy, responsibility and risk that must be adequately answered.
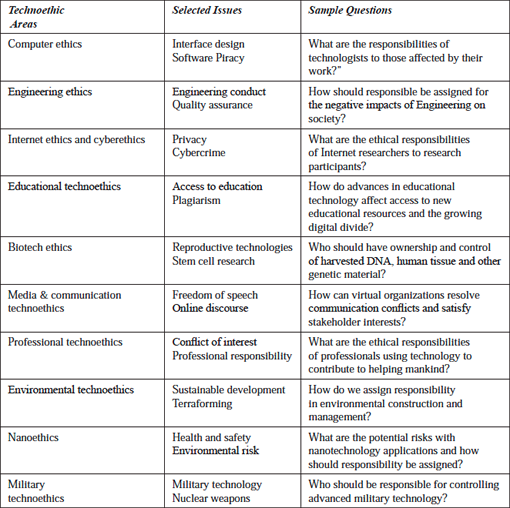
However, due to the variety of questions resulting in as much ethical inquiries that are based in different fields, there is a tendency for this knowledge to be somewhat disconnected. TE pulls this knowledge together around the central idea of technology. Moreover, unlike traditional applied ethics where focus is placed on an ethical concern for living things, TE is ‘biotechno-centric’. As the Web is to Web science, technology, as well as living things, are central in TE.
The Technoethics Way
Tracing its origins back to the late 1970s, TE emerged as an interdisciplinary field tasked with the job of answering the difficult questions posed earlier. Coined by Mario Bunge (1977), TE does not only assign technical responsibility to technologists but also gives them social and moral responsibility for their technological innovations and applications. It is believed that technologists are responsible for ensuring that their technologies are optimally efficient, not harmful and that its benefits are lasting.
This field distinguishes itself from other branches of applied ethics by elevating technology to the level of living things. However, it also builds on knowledge from wider ethical inquiry as well. TE has many sub-areas, for example, Internet, computer, biotech, cyber and nano ethics.
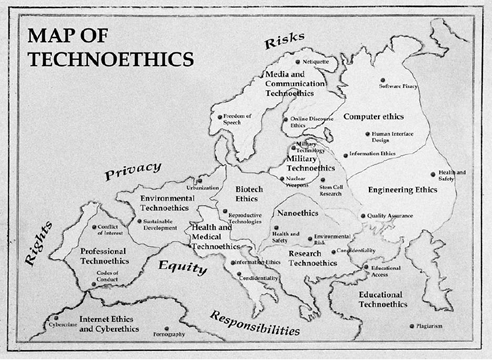
Calling All Web Scientists
Since the Web’s creation years ago, an understanding of this ever-changing phenomenon and its impact has been developing at a rapid pace in many disciplines. Yet there is a great deal more to learn, especially when the Web is positioned as the subject of focus. Considering Bunge’s views on technoethics, I believe that this obligation rests with Web scientists who are technically, morally and socially responsible for Web innovations and applications.

As a budding Web scientist, thinking about how technoethics applies to Web science, I am absolutely fascinated by all the very interesting questions that could be asked and that I could work towards answering. Ultimately, for us Web scientists, the aims of technoethics could be achieved by gaining insight into the relationship between people, the society and the Web, and how these entities impact each other.
Notes
This & Last Week’s Plan
Identifying the simplest books to read that will give an easy to understand introduction to the disciplines I picked.Making notes on books read.Prepare a blog post that gives an overview of what I want to work on.Publish a blog post that introduces technoethics.- Publish a blog post that introduces risk management.
Outline a reading plan for moving forward.
Introductory Readings
Ethics: A Very Short Introduction– Simon BlackburnHandbook fo Research on Technoethics– Rocci Luppicini & Rebecca AdellRisk: A Very Short Introduction– Baruch FischhoffFundamentals of Risk Management Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Risk Management– Paul Hopkin
EWIII: Philosophy and Law no comments
This week, I did some general reading across 3 books, though I only read one of them completely. The book I read completely was Gillies and Cailliau, How the Web was Born. This is a really good general history book of the web and just computers generally. For a non-technical and very interesting overview of where the web comes from I recommend it. They talk about TimBL’s adventures, Apple, Microsoft, Mozilla, Marc Andreeson and so on. This is a great book for someone who knows absolutely nothing about computers.
The 2 other books that I had a general look through as background reading were Boyd & Richerson, Culture and the Evolutionary Process, and David Bainbridge, Introduction to Computer Law. Boyd and Richerson are sociologists – sort of. Most sociologists hate them – and most psychologists as well, I should point out. However I think they’re great. Just because they’re unpopular doesn’t mean they’re crazy. B&R were trained as ecologists but they practically created a new ‘scientific sociology’ area all by themselves. Basically, they thought that most sociology was philosophical hogwash, and so they wanted to create something more scientific. They tried to create a theory of culture and society that was heavily informed by relevant sciences, in their case especially by the biological evolutionary sciences, particularly population genetics. They describe a theory of how information of different kinds may move through a population of people, and then they propose some equations that may be able to describe how this happens. These equations are heavily inspired by similar recursion equations proposed in population genetics, which describe how certain kinds of genetic information move through certain kinds of populations under certain conditions over periods of time. I think this is really interesting stuff. Sociologists hate B&R because they’re, well, because they’re doing something that’s hard to understand and it looks scientific. Psychologists do not like B&R very much either because it looks as if they’re trying to explain human behaviour without even bothering to refer to human psychology and cognitive processes. Personally I agree with the this 2nd criticism, but I am willing to forgive B&R for it. They weren’t trained as psychologists, and we can’t expect them to be experts on everything. Overall, I recommend B&R though they are very difficult if you are not familiar with biological evolutionary theory. I read this stuff because I am thinking of a question at the moment: to what extent should we consider the internet to be a psychological human thing? To what extent is the internet cognitive stuff? This is the sort of thing that I proposed in my application for the course.
The final book I had a look at was Bainbridge, Introduction to Internet Law. I only managed a skim through, I’m afraid, as this is a monster of a book at 500+ pages. It’s more like a textbook than anything I suppose. It looks reasonably good and not too technical, though there is a disappointing lack of pictures. This will be my main reading for next week.
Computer science and e-democracy no comments
Unlike the previous post, which briefly showed a couple of works on e-democracy from the perspective a political science specialty, this post is going to explore an overview of the entire discipline of computer science, contained in Brookshear’s Computer Science. An Overview (2009). The aim will be to start establishing initial connections to the topic and problems stated in the first post regarding technical issues in direct democracy.
In his overview, Brookshear claims that computer science has algorithms as their main object of study. More precisely, it is focused on the limits of what algorithms can do and what they cannot. Algorithms can perform a wide range of tasks and solve a wide range of problems, but there are other tasks and problems beyond the scope of algorithms. These boundaries are the area within which theoretical computer science operates. Theory of computation can therefore determine what can and what cannot be achieved by computers.
Among other issues, these theoretical considerations may apply directly to the potential problem of electoral fraud: computer science can seek for answers of whether or not algorithms can be created to alter or manipulate electoral results in a given electoral system. By establishing the limits of algorithms, an electoral system that falls beyond algorithmic capabilities can be devised in collaboration with other fields such as political science.
From the structure of the book, it can be implied that computer science also considers social repercussions in every aspect of the study of computers, as every chapter in the book contains a section of social issues that the use and development of computer technologies entails. Ethical implications are present in every step these technologies make, and computer scientists seem to be sensitive to them. Legal and political considerations are not alien to the scope of computer science. Therefore, finding a common ground with other fields such as political science for addressing certain issues in the use of information and communication technologies for a more direct democracy becomes quite achievable aim, as long as there exist a mutual effort to understand the ways in which these two disciplines deal with the problems they encounter, and the methods they use to try to solve them.
The next post will consist of a brief overview of political science, as it is the discipline that will be finally chosen –sociology will be ruled out– for this interdisciplinary essay.
Reference:
Brookshear, J.G. (2009) Computer Science. An Overview. (10th ed.) Boston: Pearson.
Anthropology – approaches and methodologies no comments
Picking up where I left off last week, I will now present the different approaches and methodologies of anthropology as a discipline.
We have already seen that social and cultural anthropology – also known as ethnography – as a discipline endeavours to answer the questions of what is unique about human beings, or how are social groups formed, etc. This clearly overlaps with many other social sciences. For all the authors reviewed, what distinguishes anthropology from other social sciences is not the subject studied, but the discipline’s approach to it. For Peoples and Bailey (2000, pp. 1 and 8), anthropological approach to its subject is threefold:
- Holistic
- Comparative
- Relativistic
The holistic perspective means that ‘no single aspect of human culture can be understood unless its relations to other aspects of the culture are explored’. It means anthropologists are looking for connections between facts or elements, striving to understand parts in the context of the whole.
The comparative approach, for Peoples and Bailey (2000, p. 8) implies that general theories about humans, societies or cultures must be tested comparatively- ie that they are ‘likely to be mistaken unless they take into account the full range of cultural diversity’ (Peoples & Bailey 2000, p. 8).
Finally the relativistic perspective means that for anthropologists no culture is inherently superior or inferior to any other. In other words, anthropologists try not to evaluate the behaviour of members of other cultures by the values and standards of their own. This is a crucial point which can be a great source of debate when studying global issues, such as the topic we will discuss on the global digital divide. And it is why I will spend one more week reviewing literature on anthropology before moving on to the other discipline of management – to see how anthropology is general applied to more global contexts. I will then try to provide a discussion on the issues engendered by the approaches detailed above.
So for Peoples and Bailey these three approaches are what distinguish anthropology from most other social sciences. For Monaghan and Just, the methodology of anthropology is its most distinguishable feature. Indeed they emphasise fieldwork – or ethnography – as what differentiates anthropology from other social sciences (Monaghan & Just 200, pp. 1-2). For them ‘participant observation’ is ‘based on the simple idea that in order to understand what people are up to, it is best to observe them by interacting intimately over a longer period of time’ (2000, p. 13). Interview is therefore the main technique to elicit and record data (Monaghan & Just 2000, p. 23). This methodological discussion is similarly found in Peoples & Bailey and Eriksen (2010, p.4) defines anthropology as ‘the comparative study of cultural and social life. Its most important method is participant observation, which consists in lengthy fieldwork in a specific social setting’. This particular methodology also poses the issues of objectivity, involvement or even advocacy. I will address these next week after further readings on anthropological perspectives in global issues, trying to assess the tensions between the global and particular, the universal and relative and where normative endeavour stand among all these.
References
Eriksen, T. H. (2010) Small Places, Large Issues: An Introduction to Social and Cultural Anthropology 3rd edition, New York: Pluto Press
Monaghan, J. and Just, P. (2000) Social and Cultural Anthropology: A Very Short Introduction, Oxford: Oxford University Press
Peoples, J. and Bailey, G. (2000) Humanity: An Introduction to Cultural Anthropology, 5th ed., Belmont: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning
Economics perspective no comments
How do web-only firms grow to build the digital economy? Which markets do they operate in? How important is the digital economy?
In macroeconomics there are a number of growth theories:
Classical growth theory: This states the view that the growth of real GDP per person is temporary and will return to subsistence level due to a population explosion.
Neoclassical growth theory: This is the proposition that real GDP per person grows because technological change induces saving and investment which makes physical capital grow. Diminishing returns end growth if technological change stops. It breaks with the classical growth theory by arguing that the opportunity cost of parenting will prohibit a rise in population.
New growth theory: This argues that the economy is a perpetual motion machine driven by the profit motive manifest in the competitive search for and deployment of innovation through discoveries and technological knowledge. Discoveries and knowledge are defined as public goods in that no one can be excluded from using them and people can use them without stopping other’s people’s use. It is argued that knowledge capital does not bring diminishing returns, i.e. it is not the case that the more free knowledge you accumulate, the less productivity is generated.
Within the microeconomics view, there are 4 market types: perfect competition in which many firms sell an identical product; monopolistic competition in which a large number of firms compete with slightly different products, leading to differentiation; oligopoly where a small number of firms compete; and monopoly in which one firm produces a unique good or service, e.g. utility suppliers.
It has been estimated by The Boston Consulting Group that the proportion of GDP in 2009 earned by the digital economy was 7.2%[1]. They estimate that it will grow to 10% in 2015. They define the elements captured by GDP as: investment, consumption, exports and Government spending. The total contribution of the internet sector divides into: 60% consumption on consumer e-commerce and consumer spending to access the internet; 40% on Government spending and private investment. They identify elements which contribute indirectly but which are ‘beyond GDP’: e.g. user-generated content, social networks, business to business e-commerce, online advertising, consumer benefits etc.
[1] The Connected Kngdomw: how the internet is transforming the U.K. economy. The Boston Consulting Group, commissioned by Google, 2010.
Complexity Science no comments
Keywords: complexity theory, complex adaptive system theory, general system theory, nonlinear dynamics, self organising, adaptive, chaos, emergent.
For the past couple of weeks I have been trying to get my head around the idea of theories of complexity as applied to systems. What is it ? How is it measured ? how does it – or does it in fact – relate to web science ?
John Cleveland in his book “Complex Adaptive Systems Theory An Introduction to the Basic Theory and Concepts” (published in 1994 revised in 2005), states that complex adaptive systems theory seeks to understand how order emerges in complex, non-linear systems such as galaxies, ecologies, markets, social systems and neural networks.
For an explanation more useful to a layman I was advised to read ‘Complexity – A guided tour’, by Professor Melanie Mitchell (Professor of Computer Science at Portland State University). In 349 pages Melanie Mitchell has tried to give a clear description and explanation of the concepts and methods which may be considered to comprise the field of Complexity Science without the use of complex mathematics.
One problem is that as a recognised discipline, Complexity Science appears to barely 30 years old, though work on some of its aspects go back to the 1930s. Mitchell suggests its beginning as an organized discipline could be dated to the founding of the Santa Fe Institute and its first conference on the economy as an evolving complex system in 1987.
Another problem appears to be that the sciences of complexity should be seen as not singular. In the last chapter of her book Mitchell comments that ‘most (researchers in the field), believe that there is not yet a science of complexity at least not in the usual sense of the word science – complex systems often seem to be a fragmented subject rather than a unified whole.’
Armed with these caveats I started ploughing my way through an interesting and enlightening book. The book is divided into five parts: background theory, life and evolution of computers, computation writ large, network thinking and conclusions – the past and future of the sciences of complexity. By the end of the book I knew more about such things as Hilberts problem, Goedels theorem, Turing machines & uncomputability, the Universal Turing machine and the Halting problem amongst others.
Below is summary of points I found interesting and have spurred further reading.
- Seemingly random behavour can emerge from deterministic systems, with no external source of the randomness.
- The behaviour of some simple, deterministic systems can be impossible to predict, even in principle, in the long term due to sensitive dependence on initial conditions.
- There is some order in chaos, seen in universal properties common to large sets of chaotic systems e.g. period doubling route to chaos and Feigenbaums constant.
- Complex systems are centrally concerned with the communication and processing of information in various forms.
- The following should be considered with regard evolution: Second law of thermodynamics, Darwinian evolution, organisation and adaption, Modern Synthesis (Mendel V’s Darwin), supportive, discrepancies, evolution by jerks, historical contingency.
- When attempting to define and measure complexity of systems Physicist Seth Lloyd 2001 asked how hard is it to decribe ? how hard is it to create ? what is it’s degree of organisation ?
- Complexity has been defined by:
- Size
- Entropy
- Algorithmic information content
- Logical depth
- Thermodynamic depth
- Statistical
- Fractal dimension
- Degree of hierarchy
- Self reproducing machines are claimed as viable e.g. Von Neumans self reproducing automaton, “a machine can reproduce itself”
- Evolutionary computing – genetic algorithms(GA), work done by John Holland, algorithm used to mean what Turing meant by definite procedure, recipre of a GA …. Interaction of different genes.
- Computation writ large and computing with particles – Cellular automata, life and the universe compared to detecting information processing structures in the behaviour of dynamical systems, applied to cellular automata evloved by use of Genetic Algorithms.
The points which seemed to be most relevant to web science and merit further investigation are:
- Genetic algoritms
- Small world networks and scale free networks
- Scale free distribution Vs normal distribution
- Network resilience
The future of complexity – mathematician Steven Strogatz “I think we may be missing the conceptual equivalent of calculus, a way of seeing the consequences of myriad interactions that define a complex system. It could be that this ultra-calculus, if it were handed to us, would be forever beyond human comprehension…”.