Posts Tagged Research
User Interface Design: How to get human visual attention by Gemma Fitzsimmons
Posted by dingran in Academic Article on May 6, 2012
Introduction
This post will describe a number of basic effects in relation to human vision and attention, focusing on how those effects can be relevant to the design of web site displays.
Saliency
Saliency is all about how much something stands out. If an object is salient, then it is more likely to attract your attention.
However, if everything is salient, it is difficult to figure out what is important and the display could be confusing. You may have already noticed this with web pages that have too much clutter, making it hard to find what you are looking for [1].
Therefore, when designing the interface to a web-based application, the items which are the most salient need to be those that are the most important to the users (e.g., buttons which are used regularly or have useful information, such as notifications).
Grouping
When a number of similar objects are close to one another, they can be visually ‘grouped’ by the user. This is particularly easy when the objects are the same colour. When ‘grouped’, they are treated as a single unit, rather than lots of single units. This makes it easier to either ignore them, or pay attention to them when necessary [2].
In the case of our project we may wish to allow the user to group feeds from different social networks together. One way to achieve this would be to colour the items according to their source (e.g., colour the backgrounds to Facebook items one colour, Twitter items a different colour and so on). This will enable the users to easily distinguish the origin of the information.
Preattentive Processing
Attention has various components. Some of these are under conscious control; others are automatic. One automatic component of attentional processing is preattentive processing. This was first described in Treisman’s Feature Integration Theory [3]. Objects will ‘pop out’ when an item in the display is salient compared to the rest of the items in the display. Examples of the many different ways an item can pop out and be detected preattentively are listed below in the image. These features can attract the users attention just because they pop out compared to the rest of the display.
User Requirement Research: Report and Analysis of Feedback
Posted by dingran in User Requirement Research on May 5, 2012
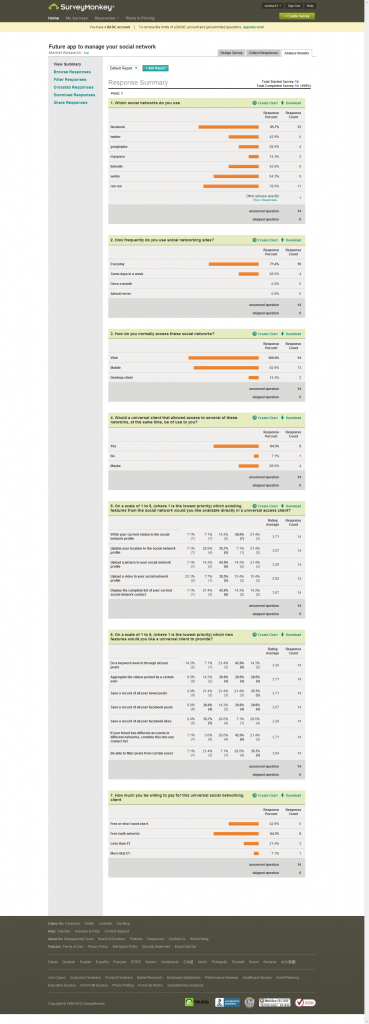
According to this survey, we finally got 14 people’s feedback. Due to most of our friends are Chinese, so sample are largely based on Chinese preferences.
However, it also provide us a basic information about what universal client people want to use
Question 1. Which social do you use now?
Most people reported that they were using Facebook (12), second rank is Ren Ren (11, a Chinese Facebook). Compared with Facebook, less people were using Twitter or Wei Bo (6 and 9), the result showing our sample is Facebook based user. By the way, a lot of user chose LinkIn as an option, a possible reason is that our sample based on ECS students so LinkIn were treated such important.
However, because only 14 people received this questionnaire, so the result means most people have two or three social network accounts at same time, which shows that a universal client could have a market for young social network users.
Question 2. How frequently do you use a social network web edition?
Most people replied that hey visited the social network everyday (10), while 4 people visited few times in a week. Those data shows young people really like to visit social network, as social network became part of their life.
Question 3. How do you normally access to those websites? By which way do you access to a social network?
People seems to treat web portal and mobile portal are same level important for them to access social network (14 and 13), while only 2 persons chose desktop client as their main way to access social network. It could be inferred that there is few desktop client is able to provide satisfied functions of social network so people rarely use desktop client. And this inspired us to design a prefect desktop client and web access portal to meet such need.
Question 4. Would you like to use any universal client that can access to multiple social networks at same time?
2/3 people believe they would like to try a universal client (9), while 1/3 people feel uncertain about this question (4). This indicated that though most people want to have a universal client to access social network, few people still doubt about the universal client. And we should release a attractive alpha edition to convert those people using universal client.
Question 5. From a scale as 1 to 5 (1 means the least and 5 means the most), please list the features that you want to access to a social network through universal client?
Excepted one option (upload video) has only 13 answers, all other options got fully answered. Base on the average weight, the most important feature people believed is the synchronize status or tweet to all social networks (3.71), secondary, people thought update location and access to full list of contactors were second important features for them (3.07). Update media from universal rank the least significant feature in this survey.
From this result, it can get two conclusions. First, most people want to user a universal client is to update a same information to multiple social networks. And second, our survey targets hold a strong interest to a mobile edition of universal client (update location and access full list of contractors are features that people normally used on a mobile terminal.), which reminds us to provide a web access portal or mobile edition is very important to our customers.
Question 6. From a scale as 1 to 5 (1 means the least and 5 means the most), please list the new features you wish a universal would have?
In this question, people gave various answers that made it is really complicated to analyze, however, such different shows that users really wish a universal client could have special and amazing features for them. As rank 1, aggregate video of specific user, save tweet and match friends are most wanted features that people wish to have (3.71). Filter post of certain user got 3.64 as second. The least feature people interested in is save ‘like’ from Facebook. And we will develop our client based on the list of most interesting features.
Question 7. How much would you like to pay for such universal client?
‘Free is the best thing in Internet Age’, as it goes, most people feel the client should be free to use (9 for free with advert and 6 for clearly free). However, few people, whom we believe they also chose free with advert shows that they want to pay 1 pound less to enjoy our service. So our strategy is using advertisement as main revenue, plus with premier account and function for those few people who would like to pay for our service to gain profit.