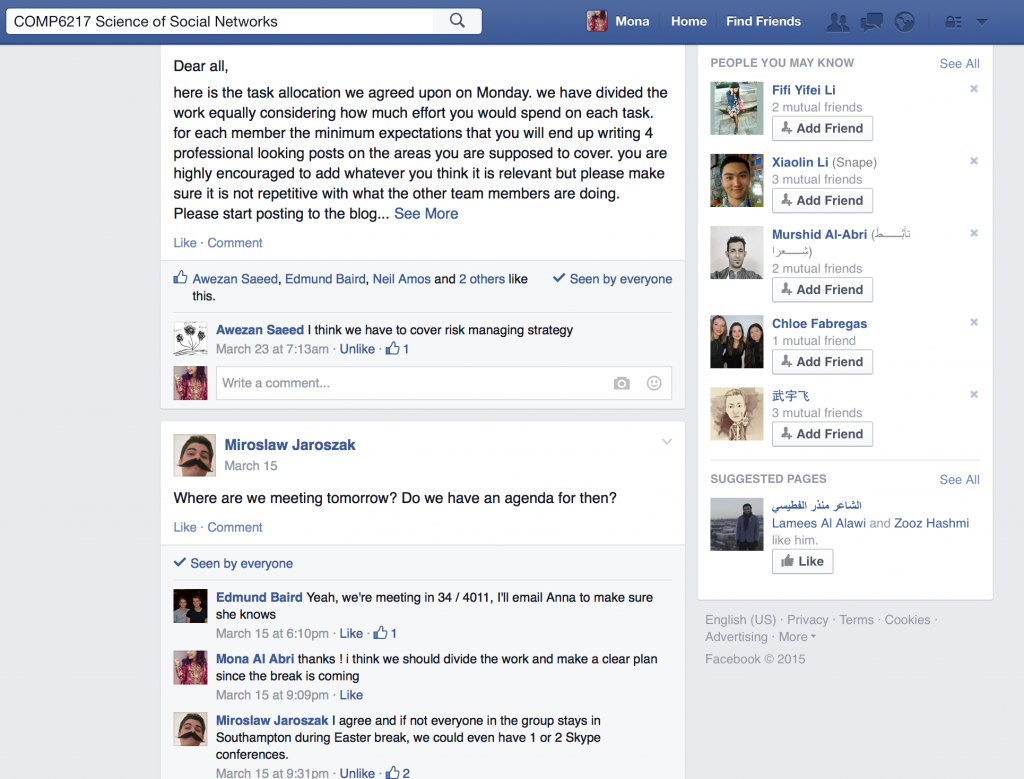
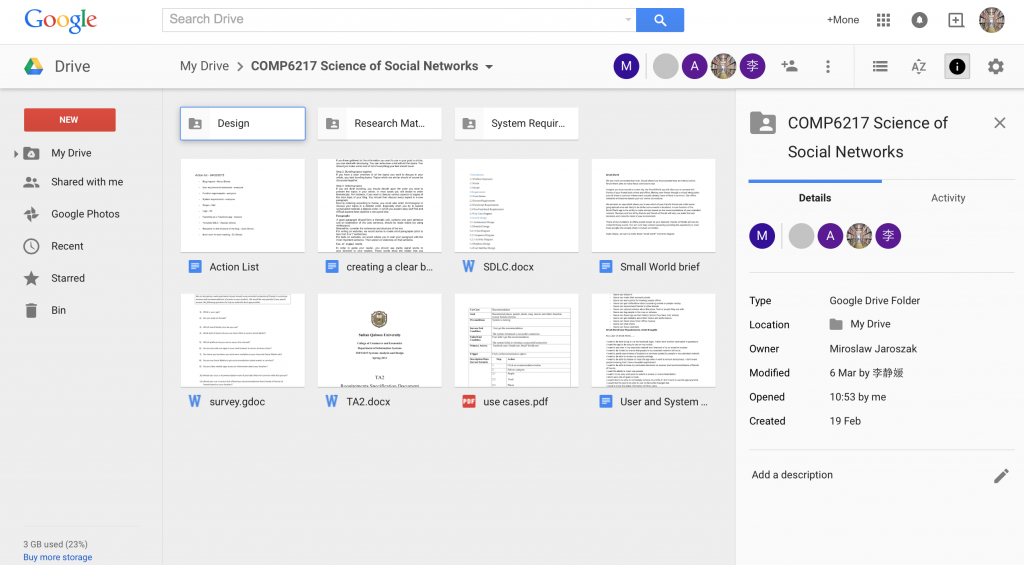
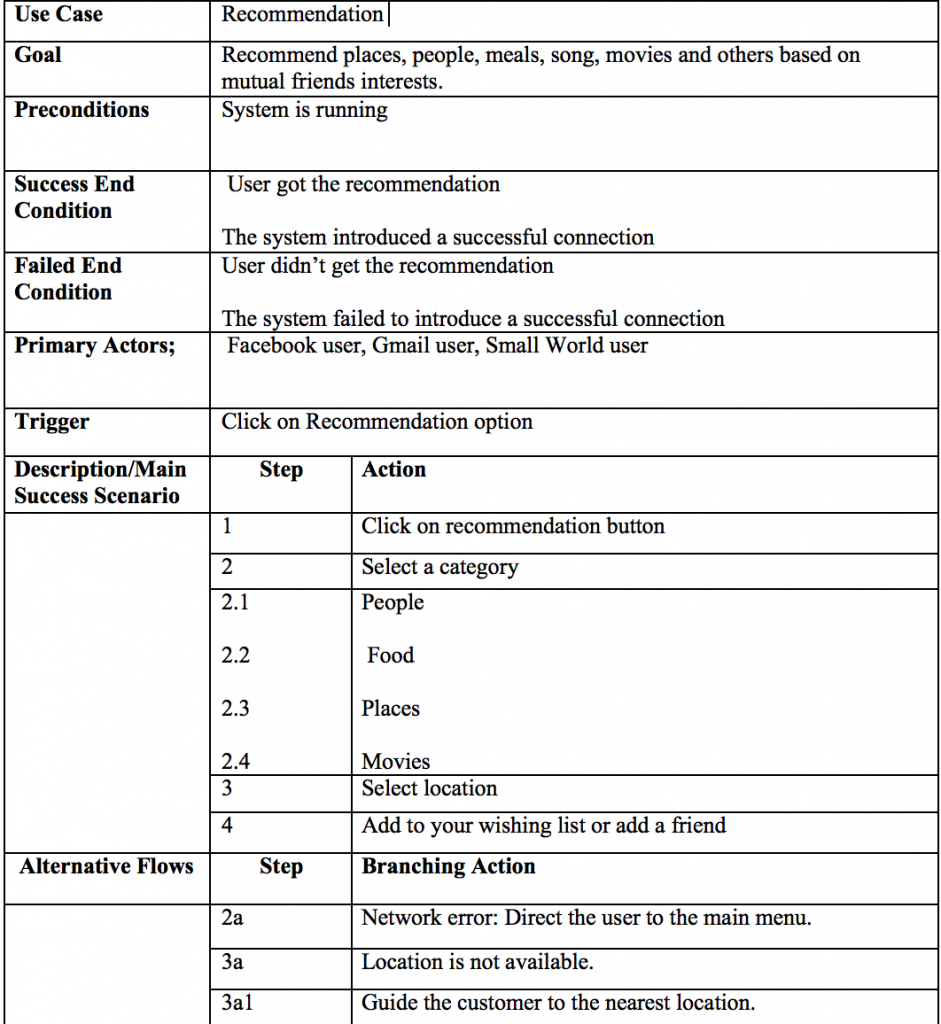
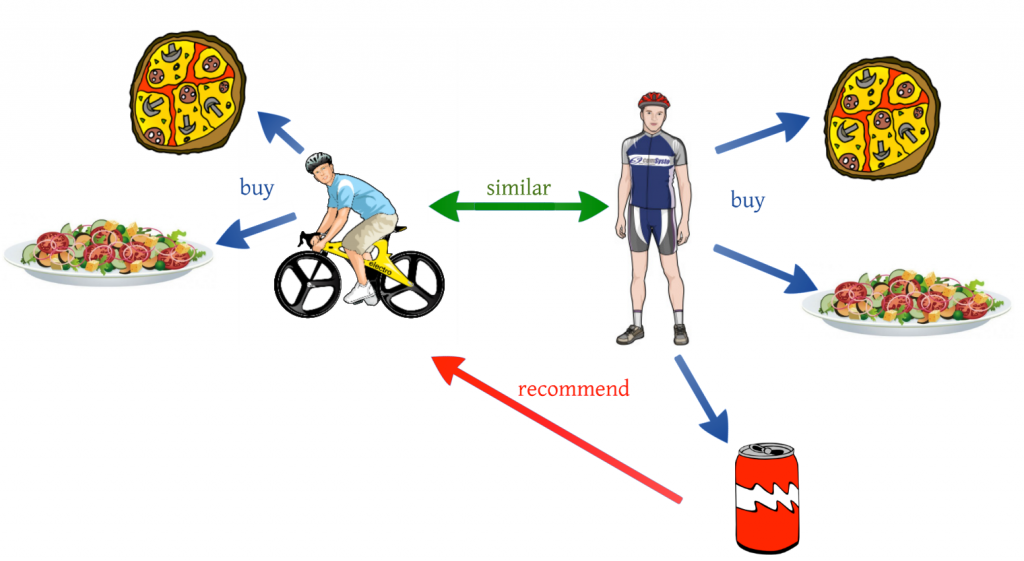
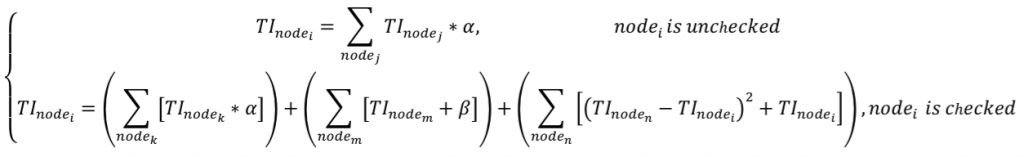Trust is involved in human activities in a daily basis. Measuring trust in a digital world can be more complicated than real life. There are various methods that help in calculating trust and evaluating users based on trust value.There are significant number of models in trust in social networks. Small.World tends to follow reputation-based trust. This comprises two type of trust:
- Global Trust: it is a quantitative approach where each user scored a value. The global trustworthiness then based on these scores.
- Local Trust: it is a qualitative approach where the trust based on personal bias (Ziegler & Lausen, 2004).
The Local Trust are following uses three properties of trust in social networks:
- Transitivity : If A trusts B and B trusts J then A will also trust J
- Asymmetry : If A trusts B it does not follow that B trusts A
- Personalization :Trust is held from the view of a node – it is therefore local trust (Millard & Imran, 2015).
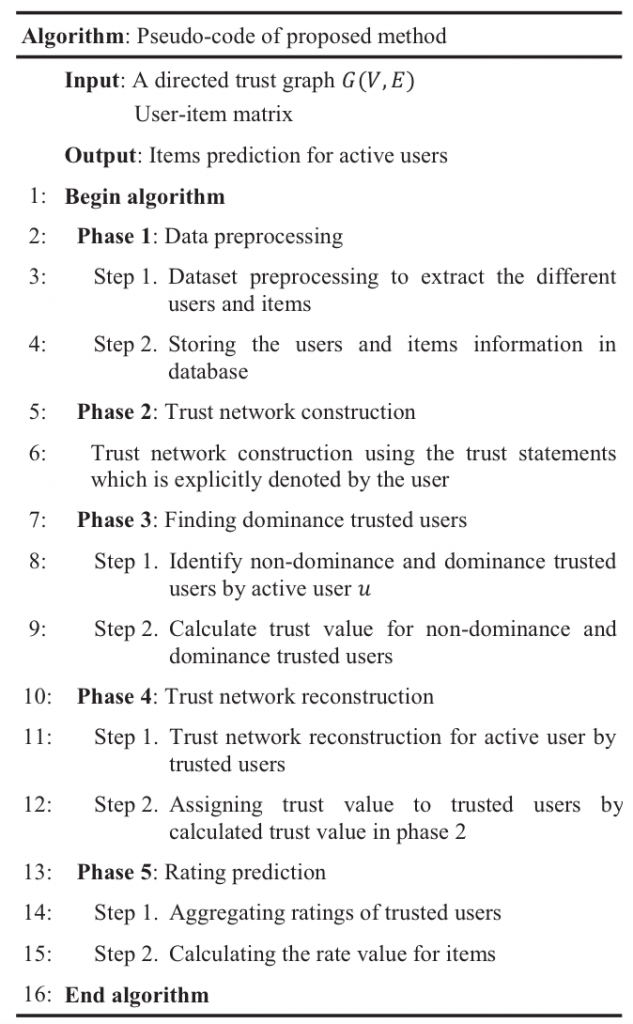
the usage of Online Social Network (OSN) trust methodologies can boost the privacy and security for the user. A user needs to know if they can trust someone to look at there profiles or how much they can trust them. The post discuss two methods: Trust-Online Social Network (T-OSN) and Trust Indexing algorithm (TI).
The evolution of OSN encouraged people to meet strangers from all over the world and become friends. But this has also, led to some problems such as identity theft and stalking. Methods that calculate trust and help users to make decisions are usually complex or require huge resources. T-OSN is a trust model that has been created specially for OSN that can also be used on other applications such as mobile message forwarding and peer-to peer file sharing network (Li and Bont, 2011).
the model is effective, simple and require the least resources possible. the model is based on two things :
1- Number of friends (Degree)
2- Contact frequency (Contact interval)
and then a user trustworthiness can be calculated for each user. The theory suggests that if a user has more friends and more frequent communication with friends, then this user is highly secure to interact with. So the user will get a higher trustworthiness.
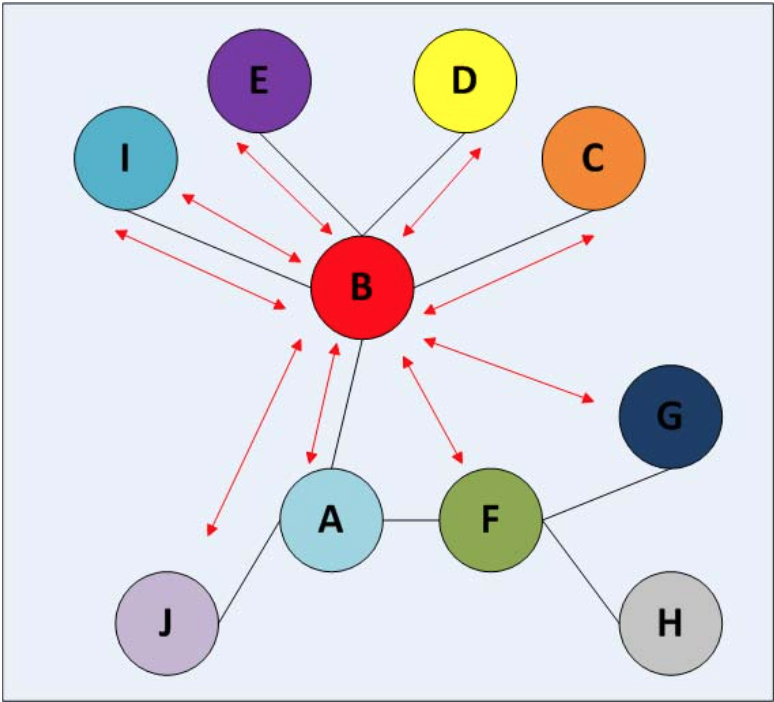
Another method is called “Trust Index” (Tang et al., 2012). It has the same idea as Page Rank that is being used in Google search engine. The algorithm is based on distance that counts hops. How far the user from his/her peer.
Each user will have a TI and a list of the ranking of other users, those who are more trustworthiness will be on the top of the ranking. The paper claims that TI successfully been able to classify trustworthiness users from those who are not (Tang et al., 2012).
Google have introduced Google+ circles where recommendations of people where based on common interests or people that the user might be connected to (Tang et al., 2012). Spam was not an issue. Small.World will follow the same path where trust will come in top of the recommendations that the users will get.
choosing a method to evaluate can be tricky where there is no ultimate solution. It depends on the type of the OSN and what factors will be involved in the algorithm.
research on this area is highly encouraged to create a more secure environment for OSN.
References:
Millard, D. and Imran, M. (2015). Trust: Part I.
Li, M. and Bont, A. (2011). T-OSN : a trust evaluation model in online social networks. In: IFIP Ninth International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing. [online] Melbourne, Australia: IEEE Computer Society, pp.469-472. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl [Accessed 12 Apr. 2015].
Tang, R., Lu, L., Zhuang, Y. and Fong, S. (2012). Not Every Friend on a Social Network Can be Trusted: An Online Trust Indexing Algorithm. In: IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conferences on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology. [online] Macau SAR, China: IEEE Computer Society, pp.280-285. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org [Accessed 12 Apr. 2015].
Ziegler, C. and Lausen, G. (2004). Spreading activation models for trust propagation. IEEE International Conference on e-Technology, e-Commerce and e-Service, 2004. EEE ’04. 2004.
This post is written by : Muna & Awezan
 The survey was planned to be distributed online using Google Forms and to a population sample of 50 people. Due to certain complications with Ergo which is the Ethical Committee in Southampton, the survey didn’t get the approval to be distributed. The team is recommending to use the survey as a future step to gather user requirements.
The survey was planned to be distributed online using Google Forms and to a population sample of 50 people. Due to certain complications with Ergo which is the Ethical Committee in Southampton, the survey didn’t get the approval to be distributed. The team is recommending to use the survey as a future step to gather user requirements.