Posts Tagged inclusion
Survey Design – Sami
Posted by Samantha Kanza in Interviews with Users or Focus Groups on March 27, 2014
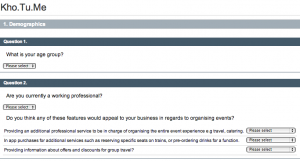
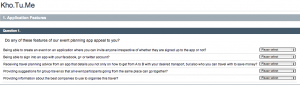
In order to assess the viability of our application, we have created a survey.
The first part of the survey creates basic demographic information, including their age group and whether they are a working professional or not. If they answer yes to working professional, then the section underneath is shown which asks them how appealing they find potential business specific features of our application. The answers in those dropdowns are “Very Appealing”, “Moderately Appealing” and “Not Appealing”.
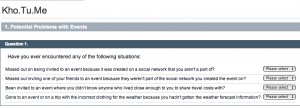
The second part is focused on looking at the problems kohtume is attempting to solve. So this section asks if any of our participants have encountered these problems when organising or going to events. These just require straight yes/no responses.
The third part is focused on seeing what features of our app are appealing to the participants. The answers in those dropdowns are “Very Appealing”, “Moderately Appealing” and “Not Appealing”.
Using a Qualitative Method to get Feedback on our Social Networking Application Idea – Sami & Someah
Posted by Samantha Kanza in Interviews with Users or Focus Groups on March 26, 2014
In order to see which elements of our social networking application are most appealing we decided to use a qualitative method to investigate this. We considered interviews, focus groups, and surveys as potential ways we could get this feedback and analysed the strengths and weaknesses of each method in relation to the time frame, and the information we wish to collect.
Focus Groups [1,2]
Strengths
- Exploring what different people have to say.
- Providing insights into the roots of complex behaviour and people’s motivations.
Weaknesses
- The moderator of the focus group can actually prove more disruptive than helpful when it comes to trying to draw opinions out of the participants.
- “polarization effect” – attitudes can become heightened and more extreme as the group discussion continues.
- Discussions can get sidelined if participants disagree strongly.
Surveys [3]
Strengths
- They are anonymous and neutral, potentially leading to more honesty.
- All of the data is collected automatically and can be analysed at a later date.
- Takes less time (in terms of direct time put towards the study).
- Can address lots of different demographics easily.
Weaknesses
- There’s a lack of engagement with the person answering the questions.
- There’s less scope to get more personalised information out of a survey, as whilst you can show different questions based on user answers, you can’t make subtle adaptions to the questions depending on how the answers are going.
- Takes more time (in terms of indirect time, of waiting for people to answer the questions).
Interviews [3, 4]
Strengths
- Qualitative interviews produce credible evidence
- It can be used to explore multiple different possibilities to answering a specific question, in addition to allowing for elaboration on certain points.
Weaknesses
- Interviews are neither as neutral or anonymous as surveys, meaning that people won’t necessarily answer as fully or honestly as they would in a more neutral surrounding where their answers could not be attributed back to them.
- There’s also a huge pressure to collect all the data needed during that interview period as otherwise that information could get lost or misrepresented when it comes to writing up the results.
- Can risk being interviewer led.
Conclusion
We wish to ask some very simple yes/no questions to find out if the problems that our social networking application attempts to address, are actually commonly occurring problems. We also wish to find out whether people find different elements of our social networking application appealing, and if so, how appealing. These characteristics seem to lend themselves best for a survey as we can ask direct yes/no questions and we aren’t looking for different interpretations or different ways to explore questions, we just want simple yes/no answers.
In addition we could run a survey cost free, and after the initial overhead of setting up the survey, it would take a lot less time to collect the data. It also allows us to target a wider demographic as we can share a survey with all of our Facebook friends, thus addressing people of different ages and professions.A survey also seems more likely to elicit participation as participants can fill in the survey at a time convenient to them, and we wouldn’t be asking for any personal information. Additionally, if we were to use the isurvey tool offered by soton, then that offers easy data analysis of results after the survey is completed.
Having taken all of these factors into consideration it seems like a survey is the most suitable for the questions we wish to ask, and the resources/time we have available.
References
[1]Sussman, S,. Burton, D., Dent, C.W., Stacy, A.W and Flay, B.R. Use of focus groups in developing an adolescent tobacco use cessation program: collective norm effects. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1991.
[2] Morgan, D.L and Krueger, R.A. When to use Focus Groups and Why. 1993.
[3] Kvale, S. Interviews. An Introduction to Qualitative Research Interviewing. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, 1996.
[4] Rubin, H.J and Rubin, I.S. Qualitative Interviewing: The Art of Hearing Data. Sage Publications, 2012.
Storyboard 3 – Jokha
Posted by Jokha Al Adi in Uncategorized on March 25, 2014
This storyboard illustrates how Koh.Tu.Me is pleasant to use, and doesn’t share your personal data against your will.
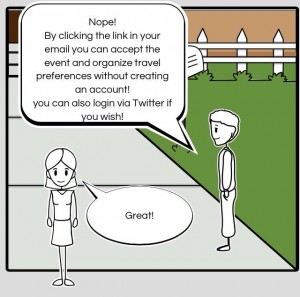
Storyboard 2 – Jokha
Posted by Jokha Al Adi in Web maps and Storyboards on March 25, 2014
This storyboard illustrates how you don’t need to create an account with Koh.Tu.Me in order to receive event invitations.
Created using: StoryBoardThat.com.
StoryBoard – Jokha
Posted by Jokha Al Adi in Web maps and Storyboards on March 24, 2014
London & Southampton Scenarios – Someah & Sami
Posted by Samantha Kanza in Scenarios and Personas on March 22, 2014
Background
Koh.Tu.Me is a Social Networking Application that is centered around bringing people together for events. It provides travel suggestions for the users so that they can travel to events with other event attendees. This blog gives examples of user scenarios of Koh.Tu.Me using the cities of London and Southampton.
London Scenario (Pleasure)
Sara has been invited to her friends wedding in the centre of London, she received the invitation from Koh.Tu.Me. She is unfamiliar with the application intricacies, but knows that it helps organise travel to events. Her main priority is to locate the cheapest public transport route she can. She puts in her home location, and the event details already contain the wedding destination, and Koh.Tu.Me shows her different transport options including:
- Underground train
- Bus
- Train
- Taxi
Koh.Tu.Me presents the times and prices of the different transport options, and a taxi number to call to receive a quote. Sarah decides to travel by bus as that is the cheapest option. Koh.Tu.Me then details her with which other event attendees will also be using that bus route so they can travel together.
Southampton Scenario (Business)
Paul lives in Winchester, and has just accepted a job working for a large company near Southampton Central Station. He has been invited to a corporate welcome event by his company using Koh.Tu.Me but naturally being new he doesn’t know anyone else working for this company, or even the best way to travel to it. He was chatting with his friends about the event, and the following conversation ensued:
Paul: “it would be really useful if I could find someone else to go to the event with me”.
Paul’s friend: “Have you seen that on Koh.Tu.Me, it provides a travel organisation service! You can choose your preferred travel option, and it will highlight which of the event attendees are also using that option so that you can travel together if you wish.
Paul says: “Oh really!! I will definitely have a look at that!”.
Paul looked at different public transport options on Koh.Tu.Me and given his company’s proximity to Southampton Central Station, and his own proximity to Winchester station it seemed like the train would be his best option. He then was shown that two other men going to the event were also going to take the train from Winchester station. All three men then met at Winchester station and bought a group travel ticket, thus enabling them to all save money, and find new travel companions for work.
Branding – Sami
Posted by Samantha Kanza in Mockups and Ideas on March 21, 2014
This post will detail the name and branding for our application.
We wanted to go for a simple catchy name, that wasn’t too difficult to say and that ideally had a meaning behind it. Thus we decided that our social networking application would be called Kohtume, which is estonian for “meet me at the” [1]. It also sounds a bit like “go to me”.
The main logo will look like this:
The logo icon will look like this:
These were chosen because we wanted the logo to be simple and illustrate our name, and based on Facebook and twitters branding, simple text based logos seem to be the fashion for social networks. We chose a bright purple to reflect “fun” [2] as that is a main purpose of our application.
This branding and colour scheme will be used in our mockups to illustrate how our application will look.
Additionally the domain kohtu.me is available [3], as we wanted to pick a name that had an available domain so our application would be easily searchable on the Web, and wouldn’t be confused with any other applications under the same name.
[1] http://mymemory.translated.net/t/Estonian/English/kohtume
[2] http://www.colorcombos.com/color-purple-article.html
[3] https://www.123-reg.co.uk/order/domain?X-CSRF-Token=a49f26b5c99f63ef2a1c9efca76486b2dd692f8e&domain=kohtu.me
Pleasure Use Case Scenarios & UML – Sami
Posted by Samantha Kanza in Scenarios and Personas, UML diagrams on March 20, 2014
This blog post will detail the Use Case Scenarios and UML diagrams for pleasure events.
NB: If you click on the images then they will direct you to a bigger version of that image.
Parties
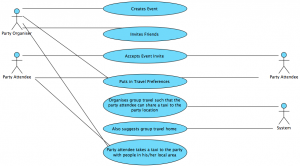
This is the Use Case Scenario and matching UML diagram for a party-esque event:
Use Case Scenario
|
Use Case Section |
Comment |
|
Use Case Name |
Organise Parties Event |
|
Primary Actor |
Party Attendee |
|
Stakeholders |
Party Attendee wants to get to the party. |
|
Preconditions |
The Party must exist and the attendee must know where/when it is. |
|
Success Guarantee
Main Success Scenario
Extensions (Other Scenarios of Success or Failure) |
The Party Attendee arrives at the correct Location at the correct time.
Extensions:
|
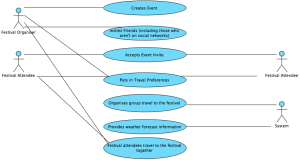
Festivals
This is the Use Case Scenario and matching UML diagram for a festival:
Use Case Scenario
|
Use Case Name |
Organise Festivals |
|
Primary Actor |
Festivals Attendee |
|
Stakeholders |
Festivals Attendee wants to get to the Festival’s location. |
|
Preconditions |
The place must exist and the attendee must know where/when it is. |
|
Success Guarantee
Main Success Scenario
Extensions (Other Scenarios of Success or Failure) |
The Festivals Attendee arrives at the correct place at the correct time.
Extensions:
|
UML Diagram
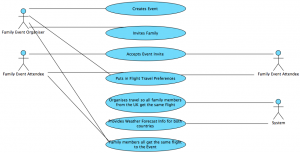
Family Events
This is the Use Case Scenario and matching UML diagram for a family event:
Use Case Scenario
|
Use Case Name |
Organise Family Events (Wedding) |
|
Primary Actor |
Family Event Attendee |
|
Stakeholders |
Family Event Attendee wants to get to the family event. |
|
Preconditions |
The event place must exist and the attendee must know where/when it is. |
|
Success Guarantee
Main Success Scenario
Extensions (Other Scenarios of Success or Failure) |
The Family Event Attendee arrives at the correct place at the correct time.
Extensions:
|
Business Use Case Scenarios & UML – Sami
Posted by Samantha Kanza in UML diagrams, Web maps and Storyboards on March 19, 2014
This blog post will detail the Use Case Scenarios and UML diagrams for pleasure events.
NB: If you click on the images then they will direct you to a bigger version of that image.
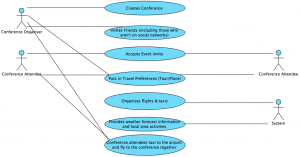
Conferences
This is the Use Case Scenario and matching UML diagram for a Conference:
Use Case Scenario
|
Use Case Section |
Comment |
|
Use Case Name |
Organise Conference Event |
|
Primary Actor |
Conference Attendee
|
|
Stakeholders |
Conference Attendee wants to get to the Conference. Conference Organiser wants the attendee’s to get to the Conference.
|
|
Preconditions |
The Conference must exist and the attendee must know where/when it is.
|
|
Success Guarantee
Main Success Scenario
Extensions (Other Scenarios of Success or Failure) |
The Conference Attendee arrives at the correct Conference at the correct time.
Extensions:
|
UML Diagram
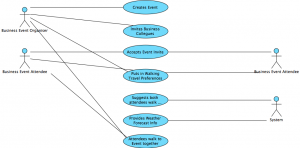
Business Day Event
This is the Use Case Scenario and matching UML diagram for a Business Day Event:
Use Case Scenario
|
Use Case Name |
Organise Business Day Event |
|
Primary Actor |
Business Event Attendee |
|
Stakeholders |
Business Event Attendee wants to get to the business event on time. Business Event Organiser wants the attendees to get to the business event on time. |
|
Preconditions |
The Business Event must exist and the attendee must know where/when it is. |
|
Success Guarantee
Main Success Scenario
Extensions (Other Scenarios of Success or Failure) |
The Business Event Attendee arrives at the correct event place at the correct time.
Extensions:
|
UML Diagram
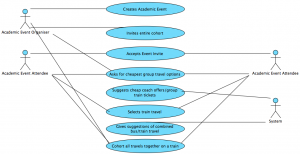
Academic Event
This is the Use Case Scenario and matching UML diagram for an Academic Event:
Use Case Scenario
|
Use Case Name |
Organise Academic Event |
|
Primary Actor |
Academic Event Attendees |
|
Stakeholders |
Academic Event Attendees want to get to the event location. Academic Event Organiser wants the attendees to get to the event location. |
|
Preconditions |
The event must exist and the attendees must know where/when it is. |
|
Success Guarantee
Main Success Scenario |
The Attendee arrives at the correct place at the correct time.
|
UML Diagram
Application Refined Version 3.0 – Sami
Posted by Samantha Kanza in Welcome and Project Brief on March 13, 2014
Event Features
The results from our business and pleasure event analysis showed that the most common features that would be useful to both business and pleasure events were:
- group travel
- multiple travel organisation (aka train then taxi)
- weather forecast information
These therefore are the main features that will be offered in the first version of our application. Future features will include:
- local area info
- accomodation
- venue booking
Login Features
In the interest of breaking down the barriers between different social networks, this application will allow logging in/signing up, in multiple different ways. In the initial version of our application login will be facilitated through:
- Login with Facebook [1]
- Login with Google Plus [2]
- Login with Twitter [3]
- Sign up to our site and create an account to login with
This means that if someone has a social networking account with any of those platforms they can still login to our application without having to create a new account.
Additionally guests can be invited to events who don’t have an account by their email address, and they will receive a link to view the event at.
In the same vein as our advertising features, this social networking app is about providing a service, and is less about collecting lots of data about the users. FOAF [4] could be used to facilitate working out who knows who for each event to make the travel planning easier, and an Address book importer [5] could be used to extract an event planners contacts to make the invite process easier.
References
[1] https://developers.facebook.com/docs/facebook-login/
[2] https://developers.google.com/+/web/signin/
[3] https://dev.twitter.com/docs/auth/sign-twitter
[4] http://www.foaf-project.org/
[5] http://stackoverflow.com/questions/87408/get-contacts-from-email-account













Recent Comments